Understanding Challenging Behaviour
- The Challenging Behaviour Foundation have a video and worksheet that explains what challenging behaviours are, why it happens, and what can be done about them.
It can be difficult to identify where a behaviour that challenges has come from, and often it may seem like it has come from out of the blue. The Challenging Behaviour Foundation has broken challenging behaviours down into different stages, which helps assess the cause of a challenging behaviour. With challenging behaviour, it is important to remember that all behaviour is communication.
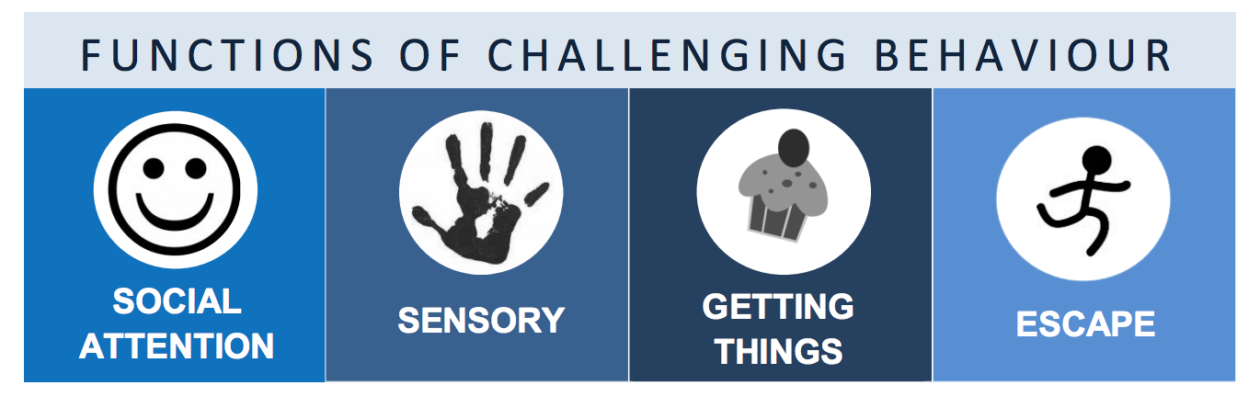
Four common functions of behaviour are:
- Social Attention
- A child may engage in a certain behaviour to gain some form of social attention from other people. The function of this behaviour might be to get other people to react, look at them, laugh at them, play with them, hug them or scold them (even when the attention is negative it can still be rewarding).
- Sensory Stimulation
- Sensory seeking behaviours function only to give the person some form of internal sensation that is pleasing to them, or to remove an internal sensation that is displeasing (e.g. pain).
- To obtain a favourite activity, object, food or drink (tangibles)
- A child may display a behaviour that challenges in order to get something that they want. If in the past they have been given a favourite activity/object or food/drink after they have displayed a behaviour that challenges, they may associate this behaviour with getting a need met/what they want.
- To escape from an activity or situation
- The behaviour may be used to indicate that the child or adult wants to end an activity or escape from a situation.
More information on the functions of challenging behaviour can be found here.

