Engineering is vital to everyday life; it shapes the world in which we live and its future. Engineers play key roles in meeting the needs of society in fields which include climate change, medicine, IT and transport.
Our society needs more engineers, and more young people with an informed view of engineering. The Course provides a broad introduction to engineering. Because of its focus on developing transferable skills, it will be of value to many learners, and particularly beneficial to learners considering a career in engineering, or one of its many branches.
National 4/5
Pupils will learn about:
- Engineering Contexts and Challenges – Learners are introduced to engineering concepts by exploring a range of engineered objects, and straightforward engineering problems and solutions. The learner explores some existing and emerging technologies and challenges, and considers implications relating to the environment, sustainable development, and, economic and social issues.
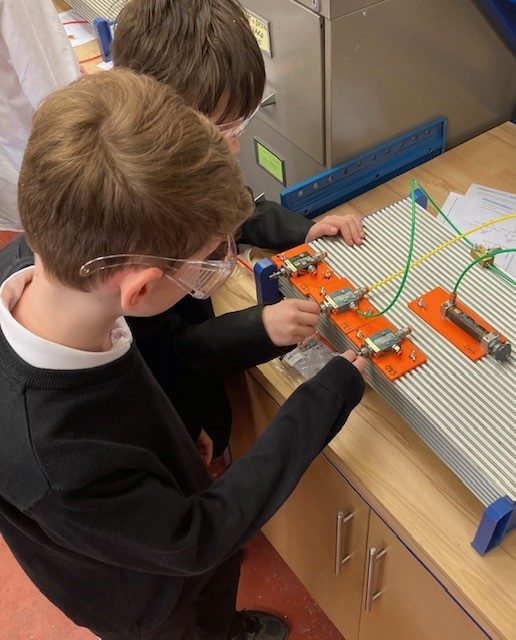
- Electronics and Control – Learners explore a range of key concepts and devices used in analogue and digital electronic control systems. Skills in problem solving are developed through simulation, practical projects and investigative tasks in a range of contexts.
- Mechanisms and Structures – Learners develop a basic understanding of simple mechanisms and structures. Skills in problem solving are developed through simulation, practical projects and investigative tasks in a range of contexts.
The subject is assessed by a combination of course assignment and an external exam, set and marked by the SQA.
Higher
Pupils will learn about:
- Electronics and Control – Learners explore a range of key concepts and devices used in analogue and digital electronic control systems. Skills in problem solving are developed through simulation, practical projects and investigative tasks in a range of contexts.
- Mechanisms and Structures – Learners develop an understanding of mechanisms and structures. Skills in problem solving are developed through simulation, practical projects and tasks in a range of contexts.
The course assessment consists of two components: an assignment and a question paper. The assignment gives learners an opportunity to demonstrate their skills in developing a solution to a set engineering task. The question paper assesses the learner’s ability to retain and integrate knowledge and understanding from across the course.

