Malcolm Wilson, ICT Curriculum Development Officer within the Curriculum Support team of Service and School Improvement, Falkirk Council Education Services, led a session at the Outdoor Learning Conference organised by Jane Jackson, Outdoor Learning Development Officer, Falkirk Council Curriculum Support Team. This session explored using mobile devices in outdoor learning.
So why use mobile devices?
Many schools are now looking to use mobile devices to enhance the educational experience of learners – whether to provide the means to explain a task, to enhance engagement of learners, to record what’s been achieved, or to facilitate sharing of learner activity with others. And many schools are also trying to make the most of the outdoors to bring learning alive. So here are ideas for using mobile devices outdoors, making use of the features of smartphones to help engage pupils in learning outdoors.
What was needed on the mobile device?
To avoid the need for an active Internet connection (to avoid pupils using their own device incurring any cost, or to avoid wifi-only tablet devices needing a connection when aweay from any signal) none of the activities described below require to use an Internet connection to operate. However prior to going outdoors the device would require to have the following features found or apps installed as required (so may require to be downloaded in advance on a wireless connection) so that they can be used outdoors where there is no WiFi availability and so that no user’s personal 3G connection data plan should incur them in a cost.
Note that the mobile device will require to have previously installed apps:
1. QR code reader to read QR codes (e.g. RedLaser)
2. Camera app (which needs to be able to take still images and video with audio)
3. Audio recorder (e.g. voice recorder)
4. Note-taking app (e.g. Notes)
5. Timer (may be a feature of a clock or alarm app)
6. Email set up with an email account which will be able to send the resulting work from the activities
How was the session organised?
 In groups of around 5, each group with one mobile device (smartphone or tablet), participants udertook a series of activities making use of apps on the mobile device.
In groups of around 5, each group with one mobile device (smartphone or tablet), participants udertook a series of activities making use of apps on the mobile device.
Each group was given a map of the school grounds with locations labelled by number or letter. Each group was given a different starting point and then rotated round locations in different sequences from the other groups. When they arrived at the noted location they found a QR code in that location. The QR code reader on the mobile device was then used to scan the QR code – this then provided written text explaining the task to be undertaken at that location.
The activities which will require to be undertaken at each location were revealed in instructions via the mobile device to each group only when they scanned the QR code with the mobile device.
For more information about the use of QR codes within an educational context see:
https://blogs.glowscotland.org.uk/fa/ICTFalkirkPrimaries/2012/03/13/qr-codes-what-are-they-and-how-can-they-be-used-in-and-out-of-the-classroom/
The site used to create the text-only QR codes for this session was https://www.unitaglive.com/qrcode
What were the activities?
Here are the task instructions which were revealed on the mobile device once each QR code was scanned. Click on the following link for the document (in Word format) with the QR codes ready for printing: QR-code_sheets-for-Outdoor_Learning_with_mobile_devices
 1. Take pictures using the mobile device camera app of the shape of each letter in the word OUTDOORS which your group will create out of materials at hand near the location (e.g. sticks, grass, stones, feet, etc). No faces should appear in the photographs.
1. Take pictures using the mobile device camera app of the shape of each letter in the word OUTDOORS which your group will create out of materials at hand near the location (e.g. sticks, grass, stones, feet, etc). No faces should appear in the photographs.
2. Take a video, lasting no longer than 30 seconds, where no faces appear, and involving everyone in the group, where each person says what they feel learners get out of outdoor learning – be creative about what you point the camera at – anything other than faces (and give it some movement so it is not static picture but scanning around) – ensure the speaking is done near the mobile device so that it can be heard clearly.
Click on this link to view a video created by one group in response to this task:
https://youtube.com/watch?v=Lkuw1x4-hHE
3. Use note-taking app on the mobile device to type words which the group comes up with which describe how you feel when looking at a view or an object outdoors which you can see where you are now – jot down the words then use the cut/copy/paste option to rearrange the words to make a rhythmic piece of writing.
One group together came up with the words: Cold, Energetic, Inspired, Mad, Creative, Moved, Free, Enthusiastic, Jealous, Carefree, Motivated, Encouraged.
Then they moved the words around on the note-taking app and created the following: “I feel Happy, I feel mad, when I’m outside I don’t feel sad I feel jealous, I feel crazy, I’m so energetic I don’t feel lazy I feel creative, I feel inspired, of the outdoors I don’t get tired!”
4. Use an audio recording app (voice recorder microphone app) to record a chant/rap made up by the group (of a few lines length), including background improvised rhythmic sounds your group creates e.g. something starting like “1-2-3-4, Get outdoors more!”
Click on the following links to hear rap/chants created by two groups in response to this task:
Outdoor Rap_LB
Outdoor_rap_CB
5. Use timer app on the mobile device to have the group collectively name as many birds in one minute as they can. Repeat this for flowers. Repeat this for trees. One member of the team acts as the timer using the app. Another member of the team counts the number of items covered in one minute each time.
One group reported they had managed the following number of items in response to this task: 20 birds, 25 flowers, 15 trees.
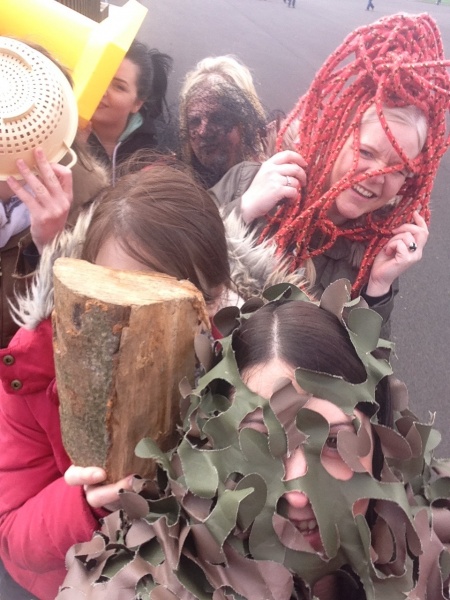 6. Create a funny “selfie” using the mobile device camera app in which everyone in the group appears (including the photographer) but where everyone’s face is obscured by objects found outdoors.
6. Create a funny “selfie” using the mobile device camera app in which everyone in the group appears (including the photographer) but where everyone’s face is obscured by objects found outdoors.
How did learners share their learning?
There are different ways of sharing materials created on a mobile device. The way which was chosen for this activity was as follows. At the end of all of the activities, once back into an environment where WiFi was available to the user of the mobile device, the resulting work was then shared by email to a single email contact. Depending on the size of attachments they may require to have been sent as separate emails rather than all at once. And in some cases in order to find the audio recordings, video, etc on the device it may be that users required to go into the individual app and click on the file, then click share and choose email as the method of sharing.
What did participants say?
Feedback from participants included:
“The ICT workshop was amazing and I learned a great deal. I can appreciate how these lessons would motivate pupils and encourage their learning and creativity.”
“Gained some ideas about using mobile technology.”
“The session with QR codes was great for a) learning how QR codes work, b) using new apps on my phone!, c) how easy it could be to use QR codes for OL activities. It supports my plans for developing our John Muir Award activities for sharing information about Polmont woods.”
“The ICT workshop in the afternoon was great fun and I could see how this could so easily be adapted for use with pupils and I can see that it would thoroughly motivate and enthuse them.”
“I enjoyed the afternoon session which gave me a better understanding of how using mobile phone with regards to children’s learning might be used”
“Doing the ICT outdoors was great fun and I came away with great ideas.”
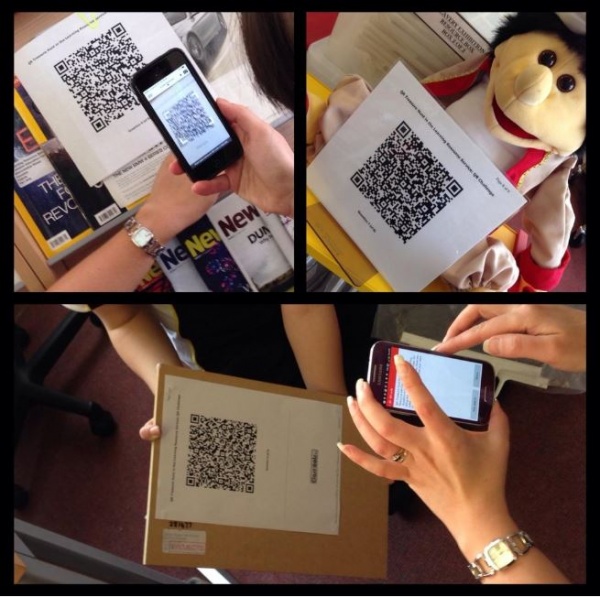 Malcolm Wilson, ICT Curriculum Development Officer within the Curriculum Support team of Service and School Improvement, Falkirk Council Education Services, presented a professional development session to teachers from several educational establishments on engaging with learning using QR codes and mobile devices. This session was supported by Yvonne Manning, Principal Librarian, Service and School Improvement Team of Falkirk Council Education Service, and colleagues within the Learning Resource Service of Falkirk Council Education Services.
Malcolm Wilson, ICT Curriculum Development Officer within the Curriculum Support team of Service and School Improvement, Falkirk Council Education Services, presented a professional development session to teachers from several educational establishments on engaging with learning using QR codes and mobile devices. This session was supported by Yvonne Manning, Principal Librarian, Service and School Improvement Team of Falkirk Council Education Service, and colleagues within the Learning Resource Service of Falkirk Council Education Services.





 Falkirk Council Education Services provides educational establishments with an Acceptable Use Policy
Falkirk Council Education Services provides educational establishments with an Acceptable Use Policy Device Neutral Assigments
Device Neutral Assigments Quick Response codes
Quick Response codes Socrative
Socrative Padlet
Padlet The Traffic Light Approach
The Traffic Light Approach