Dyslexia
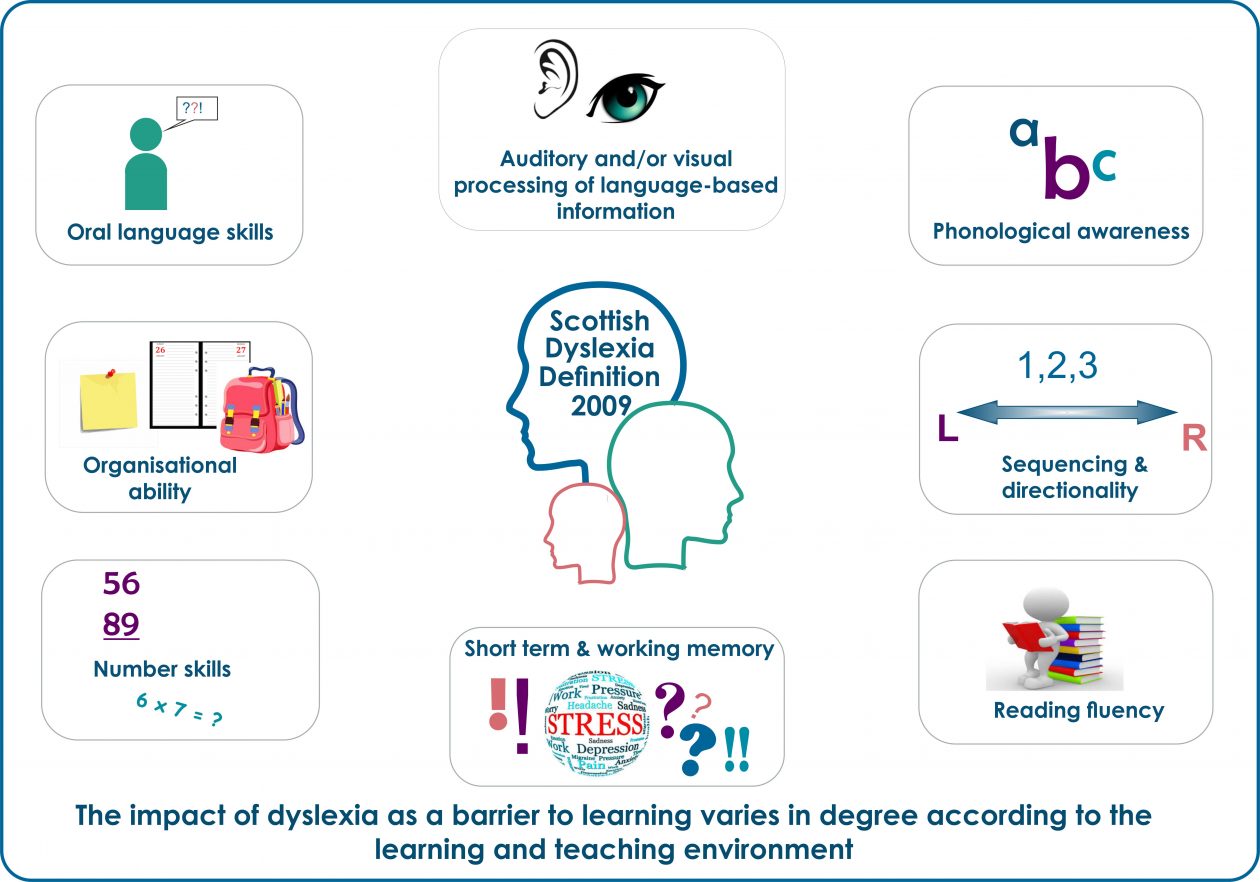
Scottish definition
Dyslexia can be described as a continuum of difficulties in learning to read, write and/or spell, which persist despite the provision of appropriate learning opportunities. These difficulties often do not reflect an individual’s cognitive abilities and may not be typical of performance in other areas.
The impact of dyslexia as a barrier to learning varies in degree according to the learning and teaching environment, as there are often associated difficulties such as:
- auditory and/or visual processing of language-based information
- phonological awareness
- oral language skills and reading fluency
- short-term and working memory
- sequencing and directionality
- number skills
- organisational ability
Motor skills and co-ordination may also be affected.
Supporting learners and families
 Effective communication, respect and partnership working are key requirements between schools and families. They are essential in supporting appropriate and effective identification, planning and monitoring of literacy difficulties and dyslexia.
Effective communication, respect and partnership working are key requirements between schools and families. They are essential in supporting appropriate and effective identification, planning and monitoring of literacy difficulties and dyslexia.
The first sign that a child/young person is experiencing difficulties with literacy or showing indications of dyslexia may arise from school staff, parents/carers or the young person. The ongoing process of identifying and supporting the needs of the learners should be clearly communicated to everyone involved.
It is important that parents and carers feel that they are being listened to, their views are valued and they are informed of all the support their child receives.
Source: Addressing Dyslexia
IMPORTANT: You will find a lot of information, from dyslexia friendly formats to ideas for supporting reading and study skills by clicking here.
Find out more:
Addressing Dyslexia
Dyslexia Scotland
Strategies and Resources
Dyslexia Identification Pathway
At Home with Dyslexia Scotland

