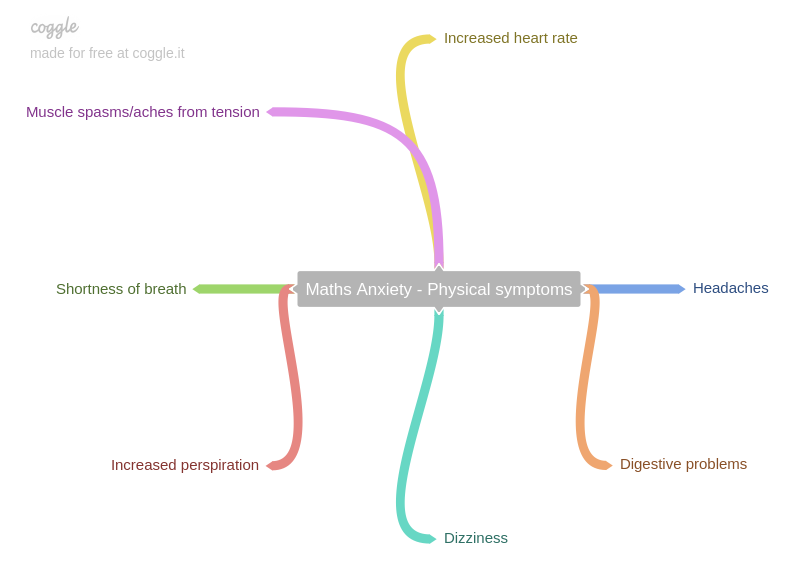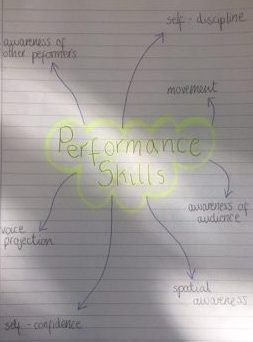
After creating a breakdown of performance skills which are represented on a mind map (see above), I have chosen to specifically focus on the aspect of self-confidence. Attached below is a lesson plan which focuses on building up the self-confidence of pupils in the area of drama.
This aspect was selected as a child’s self-confidence is an incredibly important part of their whole being. To have self-confidence means that a person believes in themselves – in their own abilities, qualities and decisions. As such, they are often assertive, positive and self-reliant. However, self-confidence is a fragile thing and needs to be nurtured in order to help a child feel able to express themselves which, in turn will help them survive and hopefully succeed in life. Equally, it is important not to damage a child’s self-confidence as this could also have major repercussions, making them feel worthless, withdrawn and unable to face challenges in later life. This aspect is obviously important in the area of drama but it is also clearly a crucial skill which can support pupils in their wider lives. Having self-confidence can help a person feel like they can take on or face the world with energy and determination and this in turn, can result in better relationships, help with getting a job and ultimately a more secure, settled life.
The lesson plan outlines a lesson which focuses on students developing self-confidence by encouraging the pupils to express themselves verbally and physically in front of their peers. Activities for this include games, role-playing and the presentation of short group improvisations. The games activity was introduced at the start of the lesson to try and make the pupils relax and loosen up so that they felt more at ease when speaking in front of the class. Having the games at the beginning also helps to start the lesson off on a high note with something fun, involving a lot of laughter and smiles. Likewise, the role-playing and presentation of improvisations were done in groups to avoid pupils feeling uncomfortable and under too much pressure if they had to perform by themselves. Using groups for the first lesson will then provide a stepping-stone for more drama lessons or productions with individual work to come.
Below is the lesson plan:
Individual Lesson Plan Format (Primary)
Class/Group: …class…lesson…… Lesson: …Drama………… Date: ………..…
| Previous Experience
|
||||||
| Working towards outcomes of a Curriculum for Excellence
I have experienced the energy and excitement of presenting/performing for audiences and being part of an audience for other people’s presentations/performances. (EXA 2-01a) I have created and presented scripted or improvised drama, beginning to take account of audience and atmosphere. (EXA 2-14a) |
||||||
| Responsibility of all – Literacy/Numeracy/ICT/HWB (where appropriate): Expressive Arts – Drama | ||||||
| Learning Intentions | Success Criteria | |||||
| WALT (we are learning to)We are learning to role play short scenes |
WILF (what I’m looking for)- Voice projection and expression- Awareness of audience- Awareness of other actors/actresses – Spatial awareness |
|||||
| Resources | Chairs, backstage description group cards | |||||
| Timing | 1 hour | Assessment methods | ||||
|
0 – 5
5 – 15
15 – 30
30 – 45
45 – 55
55 – 60
|
Setting the context/Beginning the lesson (Introduction)
How confident do you feel performing to the class in a group? Class spaced out standing in a circle Game of Splat Game of Zip, Zap, Boing
Teaching the learning intentions (Development) Park Bench Activity – Class sit down on carpet – two chairs put on stage area – one volunteer (teacher join in with example) Aim of the exercise is to try and force the other person to leave the park bench. one pupil pretends to start chewing gum very loudly with mouth open right next to the volunteer’s ear. Takes gum out and puts it under the bench. Finds two pieces of used gum underneath the bench, asks volunteer if they want a bit. Puts used gum in mouth. The volunteer would have to be honest and decide whether this would make them leave the bench or not. This game would carry on getting a new volunteer every time the person leaves the park bench.
Group work Split the class into 9 groups // approximately 4/5 per group (depending the size of the class) Each group are given a card – depending on size of class, groups may be given two cards. Each group must act out what is on their card. They have the choice of either acting out a short scene demonstrating what the card says, creating a still image or acting out a mime. The teacher will go around each group and will discuss what each card means to make sure the groups are on the right track. Each group will demonstrate what they have created to the class.
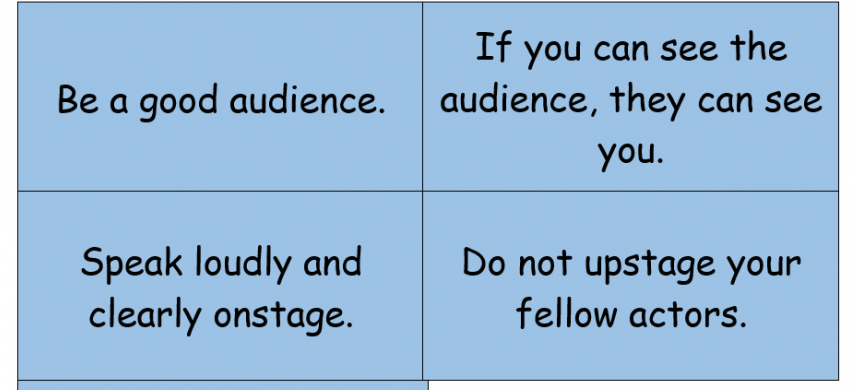
Ending the lesson (Plenary) After our lesson are you feeling more confident performing in front of the class? |
Observation of how many fingers from each student
Observation of participation, big arms, loud voices
Observation of listening skills
Observation of volunteers
Observation of creativity
Observation of teamwork skills
Observation of who is being a good audience
Observation of group work and confidence within the performances
Observation of thumbs to see if there has been improvement after lesson |
||||
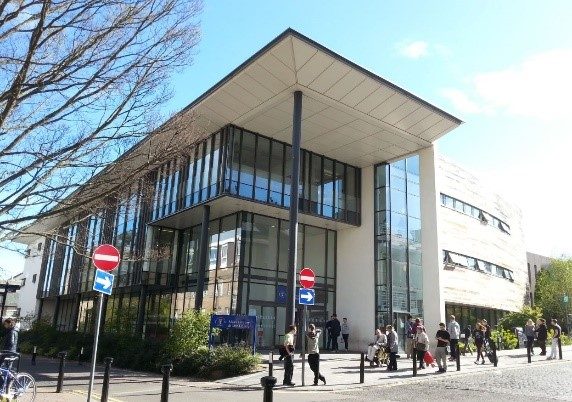


 building and make full use of it. This central position also reinforces and perhaps symbolizes the importance of reading and research which lies at the heart of university study. Having the library positioned close to the student Union and the Premier is also convenient for students whether they are needing to buy snacks, paper or need a change of scenery for a lunch break.
building and make full use of it. This central position also reinforces and perhaps symbolizes the importance of reading and research which lies at the heart of university study. Having the library positioned close to the student Union and the Premier is also convenient for students whether they are needing to buy snacks, paper or need a change of scenery for a lunch break. with stone and a wood-like material. This ensures that the building blends in well with its surroundings and the neighbouring buildings close by.
with stone and a wood-like material. This ensures that the building blends in well with its surroundings and the neighbouring buildings close by.

 of the library follow the theme of a rainforest, with a green, pastel yellow and white colour scheme. This is actually my favourite floor as the nature theme creates a feeling of relaxation, peace and tranquillity. As such, it provides a positive atmosphere for students who are trying to study, making this floor fit for its purpose.
of the library follow the theme of a rainforest, with a green, pastel yellow and white colour scheme. This is actually my favourite floor as the nature theme creates a feeling of relaxation, peace and tranquillity. As such, it provides a positive atmosphere for students who are trying to study, making this floor fit for its purpose. The second floor is the top floor of the library and is a completely silent area to work in. This floor is very basic with single desks spread out. Likewise, the colour scheme is a basic brown and white. Whilst not particularly aesthetically pleasing, it does create a business-like, no-nonsense type of environment where there are no distractions. This is also fit for purpose as it is useful for some students because it helps them to focus on the study task.
The second floor is the top floor of the library and is a completely silent area to work in. This floor is very basic with single desks spread out. Likewise, the colour scheme is a basic brown and white. Whilst not particularly aesthetically pleasing, it does create a business-like, no-nonsense type of environment where there are no distractions. This is also fit for purpose as it is useful for some students because it helps them to focus on the study task. lot of large glass windows. This allows natural light in to keep it bright, giving it a modern, airy feel yet still fitting in well with the rest of the university campus.
lot of large glass windows. This allows natural light in to keep it bright, giving it a modern, airy feel yet still fitting in well with the rest of the university campus.
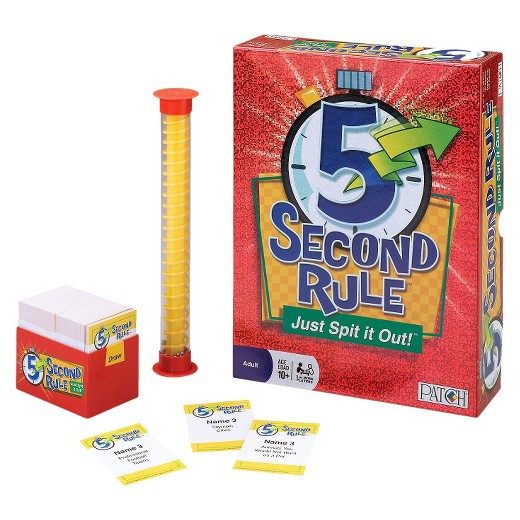 behind the game. On my table we had ‘The 5 Second Rule Mini Game’. This is a quick thinking and fast-talking game which puts the chosen individual under pressure. The question master will ask a question, for example, “Name 3 foods beginning with the letter ‘c’?”. The timer will be turned, and the chosen individual has five seconds to answer the question. This frantic game puts you under pressure and can make your mind go blank with the fast pace and the pressure!
behind the game. On my table we had ‘The 5 Second Rule Mini Game’. This is a quick thinking and fast-talking game which puts the chosen individual under pressure. The question master will ask a question, for example, “Name 3 foods beginning with the letter ‘c’?”. The timer will be turned, and the chosen individual has five seconds to answer the question. This frantic game puts you under pressure and can make your mind go blank with the fast pace and the pressure!





 After doing research I realised the many connections field hockey has to maths. The design of the pitch is in the shape of rectangle which is separated into four sections. There are 3 lines marked across the pitch marking the 25m line, the 50m line (half pitch) and the 75m line. A hockey pitch also consists of two semi circles that make out 180 degrees which is called the “d”.
After doing research I realised the many connections field hockey has to maths. The design of the pitch is in the shape of rectangle which is separated into four sections. There are 3 lines marked across the pitch marking the 25m line, the 50m line (half pitch) and the 75m line. A hockey pitch also consists of two semi circles that make out 180 degrees which is called the “d”.