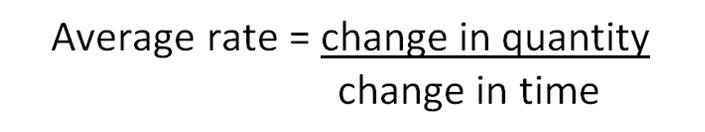The rate of a reaction is usually thought of as the change in the concentration of products or reactants over time. In those reactions where the change in quantity is easily measured, the average rate of reaction can be calculated:
Average Rate is expressed in units such as g s-1, cm3 s-1 or mol l-1 s-1.
Relative Rate:
However, it can be difficult to measure the product being produced or reactant used up – possibly because the reaction is very quick. The time taken for the reaction to complete can be used to calculate the relative rate of reaction. This is found by taking the reciprocal of the time to complete the reaction (1/t):
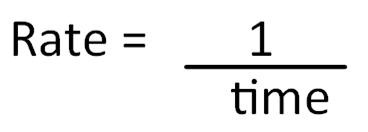
Relative rate of reaction is therefore expressed in units such as s-1 (per second).
Measuring rate of Reaction
A variety of methods can be used to measure the rate of a chemical reaction. The choice of method will depend on the nature of the changes in the chemical reaction.