Light and Radiation Summary
Light is a form of energy and it always travels in straight lines.
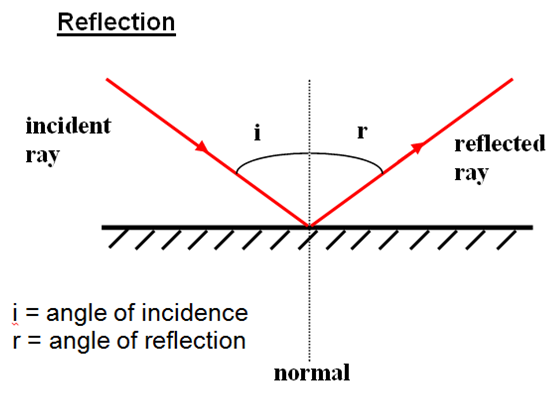 When light is shone onto a reflective surface at an angle, it will reflect off it at the same angle.
When light is shone onto a reflective surface at an angle, it will reflect off it at the same angle.
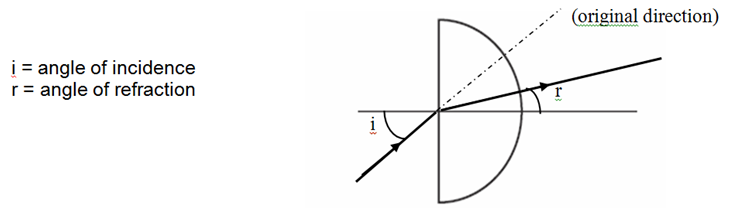
Angle of incidence = Angle of reflection.
The angle of incidence is measured between the incident ray and the normal. The angle of reflection is measured between the reflected ray and the normal
Refraction
When light travels from one material to another (e.g air into glass), the light can change direction. This change of direction is known as refraction. The angle of refraction inside the glass will be smaller than the angle of incidence in air. We say that the light bends towards the Normal.
Prisms
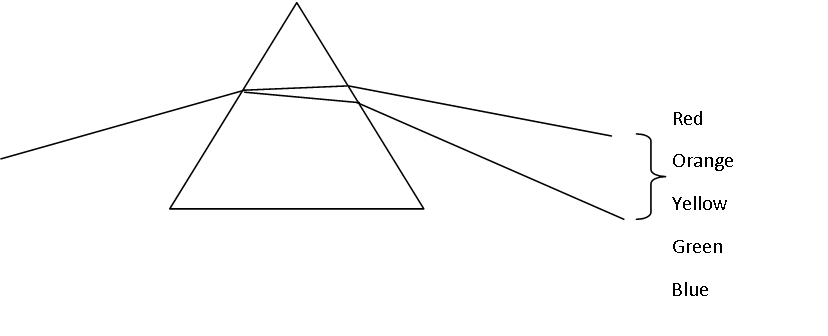
When white light is passed through a prism; it produces a spectrum.
The spectrum is a continuous spread of colours and is the same spread of colours you see in a rainbow.
The mnemonic Richard Of York Gave Battle In Vain can be used to remember the order of the colours Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Indigo, Violet.
Coloured Filters
Filters can be used to produce different colours of light when white light is passed through it. They work by allowing the colour of light appropriate to the filter through but absorb all the other colours that make up white light. For example, a green filter allows green light through but absorbs red, orange, yellow, blue, indigo and violet.
Red, green and blue filters can be used with white light in colour mixing to produce other colours.
Red + Green = Yellow
Red + Blue = Magenta
Blue + Green = Cyan
Red + Green + Blue = White
Shining Light onto Coloured Surfaces
The colour seen by the human eye depends on two factors: The colour of light shining and the colour of object the light is shining on.
A green car appears green in white light because it reflects green light and absorbs red and blue.
Lenses
Convex lenses (surface curves ‘out’) make rays of light converge (come together)
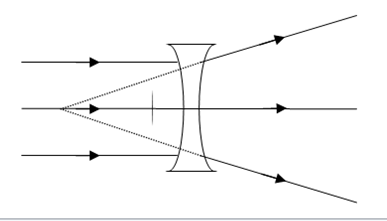
Concave lenses (surface curves ‘in’) make rays of light diverge (move apart)
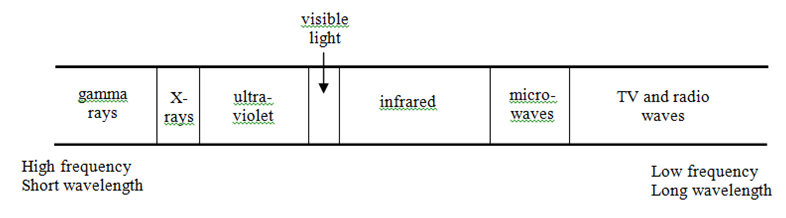
The Electromagnetic (e-m) Spectrum
The e-m spectrum is a “family” of waves all travelling at the speed of light (3×108 m/s). These radiations have different wavelengths and frequencies.
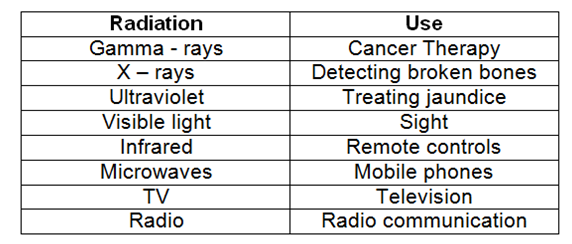
The different radiations have unique properties and can be used in different ways: