- Database structure: field, record, file
- Database structure: flat file, linked tables, primary keys, foreign keys
- Field types (text, numbers, date, time, graphic, object, calculated, link, boolean)
- Validation (presence check, restricted choice, field length, range)
- Database operations search, sort (on multiple fields)
- Good design to avoid data duplication and modification errors (insert, delete, update)
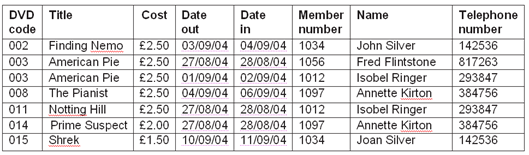
Database structure
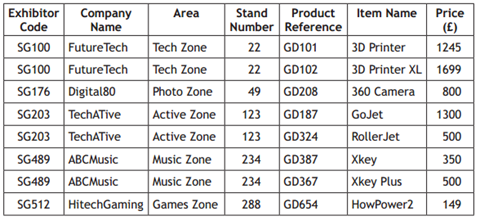
- field – the fields below; Exhibitor, Company Name, Area, Stand Number, Product Reference, Item Name, Price (£)
- record – A single row in a table, there are 8 records below
- file – the entire database
- flat file all the data is stored in one table
- Drawbacks Data duplication Data inconsistency or update/ deletion/insertion anomalies Data integrity errors (due to data inconsistency) Inconsistent search results in multi-value fields
- linked tables data is stored in tables that are linked together.
- The table above would be split into
- EXHIBITOR(Exhibitor Code, Company Name, Area) P
- RODUCT(Product Ref, Item name, Price (£), Exhibitor Code*)
- primary keys – these are unique identifiers for each row in a table
- foreign keys* – a primary key from a different table
Database operations
- Simple search – a search on ABC Music would return the following

- Complex search – Searching on two (or more) fields at once for example
- Company name = FutureTech and Price > 1500 would return the following

- Simple sort – Sorting a table by one field, class registers are sorted by surname
- Allan, Tom
- Bennet, Gordon
- Clark, Petula
- Donaldson, Luke
- Elliot, Paula
- Complex sort – same as above but if two people have the same second name they are sorted by first name as well
- Allan, Tom
- Bennet, Gordon
- Clark, Petula
- Donaldson, Luke
- Elliot, Paula
- Ferguson, Alex
- Ferguson, Sarah
- This is in Alphabetical or Ascending order
Field types
- text – A Roberts, ML1 3XF
- numbers – 124
- date – 29 April 2012
- time – 08:30
- object – Picture, video or sound file.
- calculated – pay * 20%
- link – www.bbc.co.uk
- Boolean – either yes or no
Validation
- presence check – data must be entered before the user can continue, usually has a star.
- restricted choice – please see below, the user can only select one option.
Benefits
- Reduces the chance of human error
- Does not require the user to type a text response
- Speeds up the ordering process as inputs are reduced to mouse clicks
- Allows the use of a touchscreen
Design
Good design to avoid data duplication and modification errors (insert, delete, update)
Flat file databases can lead to errors as shown below
Is Member Number 1034 a man called John Silver or a woman called Joan Silver?