Standard file formats:
- Text:
- txt – only text stored no formatting
- rtf – Rich Text Format, text and formatting stored, new standard allow for the storing of embedded images.
- Audio:
- wav – uncompressed audio
- mp3 – compressed audio
- Graphics:
- jpeg – used for photographs due to strong compression
- bmp – uncompressed
- gif – used for animations and drawings, few colours
- png – compressed with partial transparency.
- Video:
- mp4 – compressed
- avi – uncompressed
- Pdf: Portable Document Format – used to retain the look and format of a document across difference platforms. Document always looks the same regardless of screen size, fonts etc.
Factors affecting file size and quality
- Resolution – the number of pixels used to make up the picture.
- Colour Depth – the number of possible colours used to make up a pixel. The more possible colours the greater the file size.
- Sampling Rate – in sound files the number of recordings taken per second., the greater the sample rate the higher the quality and file size.
Calculation of file size for colour bitmap.
Horizontal Pixels = image width x resolution(DPI)
Vertical Pixels = image height x resolution(DPI)
Number of pixels = Horizontal Pixels x Vertical Pixels
File Size = Number of pixels x colour depth (in bits)
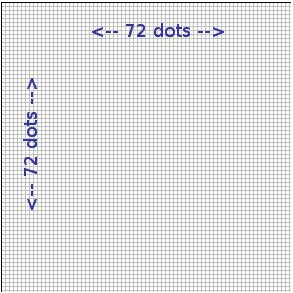
Example 1
This is enlarged but is 1 inch by 1 inch.
In that case there are 72 x 1 x 72 x 1 = 5184 pixels
Example 2
Bitmap with a resolution of 600×600 pixels in 8 bit colour.
Storage requirements
600 x 600 x 1 bytes = 360000
It is 1 byte as it is 8 bits per pixel
360000/1024 = 351.6 kilobytes
Example 3
Calculate the number of pixels in 4 inch by 5 inch photograph scanned which has a resolution of 600 dots per inch.
Pixels = 4 x 600 x 5 x 600 = 7,200,000 bits
7,200,000 / 8 = 90000 bytes
90000 bytes / 1024 = 878.9 Kb
Vector Graphics
It is possible to edit each object separately, for example, change the shape, colour, size and position.
Even if an object in a vector graphic is quite large, it doesn’t need a lot of computer memory. Therefore the file size of a vector graphic is often very small.
Vector graphics are scalable when you resize them, they do not lose quality.
Need for compression – reduces the file size so that the web page loads more quickly. Reducing bit depth has the same impact. Quality of the image is affected.