![]()
Quality Assurance
What is it?
Quality assurance is a range of monitoring, moderation and evaluation activities that help settings assess the quality of the service for children and families.
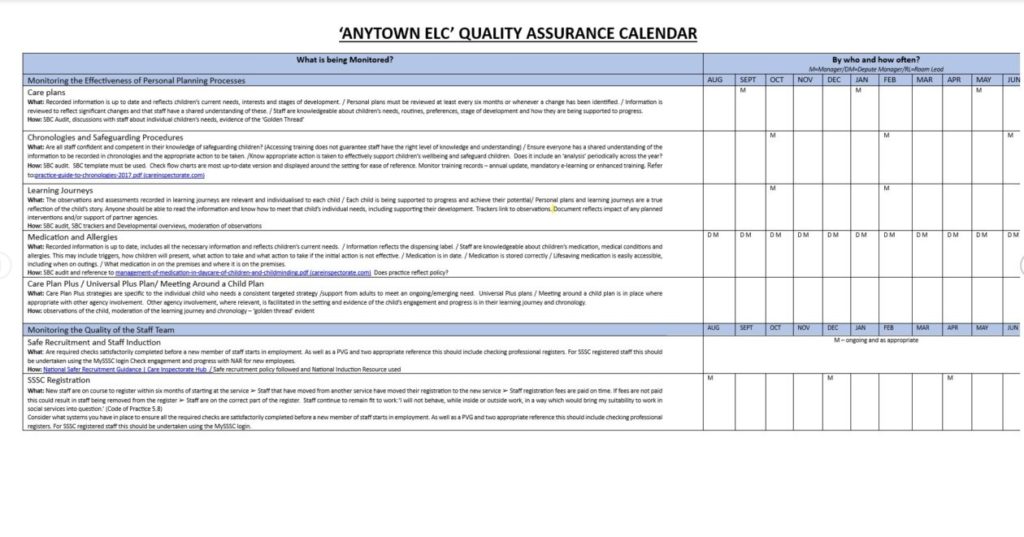
A quality assurance calendar helps leaders map out what aspects of practice will be monitored, moderated, or evaluated to determine if a high-quality service is being provided.
Practitioners then need to take action when quality falls short or identify strong practice that can be further built upon.
Immediate action would be relevant to issues of quality, particularly where children’s safety or wellbeing is compromised. For example, a quality assurance activity highlights that nappy changing procedures are not being followed consistently by all staff which is leading to compromised infection prevention and control procedures. This presents a hygiene risk so immediate action needs to be taken.
Longer term action could form an improvement agenda and could be taken forward through a focus in the setting improvement plan.
How does quality assurance link to self-evaluation?
Regular and effective self-evaluation against a range of frameworks requires practitioners to reflect on their practice and use a range of information to make informed decisions about how well the setting is doing and what needs to improve.
Children, families and partners views must be taken into account when evaluating aspects of practice and when planning for improvement.
Those views, together with the evidence from quality assurance and other relevant activities, help settings effectively and robustly self-evaluate.
Key messages about effective quality assurance:
An effective quality assurance calendar should:
-
- Be set out what is being monitored, moderated or evaluated
- Indicate how it will be done (the activities that will be done)
- Indicate the month/date the activity will be completed
- Name the practitioner responsible for completing that activity
- Reflect the needs of your service at the time of planning the calendar
- Be flexible to take account of emerging needs which may not have been identified at the time of planning the calendar
- Identify strengths and areas of practice that need to improve
- Be followed up as appropriate – minutes of staff meetings, or quality assurance or self-evaluation, or setting improvement floor books, are good ways to evidence strengths and/or any action being taken as a result of quality assurance activities and the impact it has had on children
Resources
Spotlight on Practice
Quality Assurance
Fiona Duncan-Kerr, funded childminder in SBC, shares her approach to quality assurance, self-evaluation & monitoring the impact of training on outcomes for children.