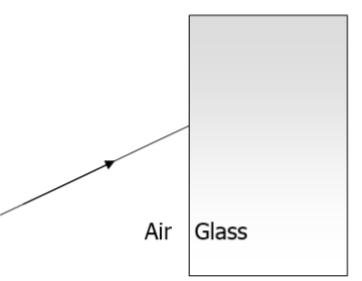
1. A ray of light passes from air to glass as shown:
(a) Copy and complete the diagram to show the path of the ray of light through the block and after it emerges from the block.
(b) Label the angle of incidence and angle of refraction.
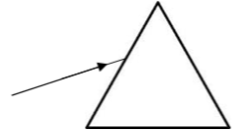
2. Copy and complete the diagram to show the path of the ray through the triangular prism and back out into the air.
3. What does ‘refraction’ mean?
4. State the speed of light as it passes through glass.
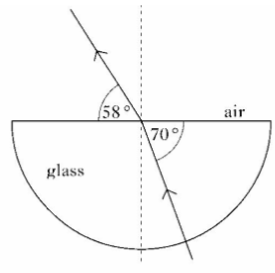
5. A ray of light passes through a glass block as shown below.
State the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction.
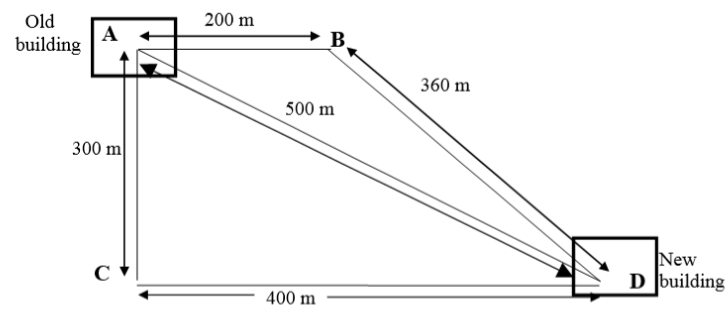
6. A high street bank decides to extend their premises and move into a second building near their main branch. In order to pass information from one building to the other they lay fibre optic cables to link them. The most cost effective way to do this is to lay the cables along existing pathways.
The map below shows the different ways the cable could be laid.
(a) Along which route should the cable be laid to ensure that data is passed as quickly as possible? (Use the letters on the diagram)
(b) If the speed of light along the cables is 2 x 108m/s, calculate the time delay between sending and receiving the information along this route.
(c) An engineer surveying the pathways suggests it would be cheaper to lay cables along route A-B-D. What extra time delay in receiving information would this involve?