1.
Materials X and Y are radioactive and their respective half lives are 20 minutes and 30 minutes. At the start of an experiment the activity of material X is 8 000 Bq while the activity of Y is 2000 Bq.
How much time will elapse, from the start of the experiment, before the activities of materials X and Y are equal?
2. The diagram shows a machine that emits nuclear radiation to treat bone cancer.
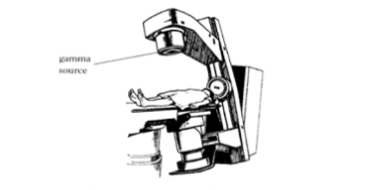
(a) Cancer cells are living cells that grow abnormally.
(i) What is the effect of nuclear radiation on cancer cells?
(ii) The machine emits gamma radiation. Explain why gamma radiation is used rather than alpha or beta radiation.
(iii) Explain why the gamma radiation source is rotated around the patient.
3. Name the main nuclear process taking place in the Sun.
4. Describe (with the aid of a diagram) what is meant in nuclear physics by a ‘chain reaction’.
5. Gold-198 is a radioactive source that is used to trace factory waste which may cause river pollution. A small quantity of the radioactive gold is added into the waste as it enters the river. Scanning the river using radiation detectors allows scientists to trace where the waste has travelled. Gold-198 has a half-life of 2.7 days.
(a) What is meant by the term “half-life”?
(b) A sample of Gold-198 has an activity of 64kBq when first obtained by the scientists. Calculate the activity after 13.5 days.
(c) A scientist receives an absorbed dose of 10 mGy of alpha radiation.
(i) Calculate the equivalent dose received.
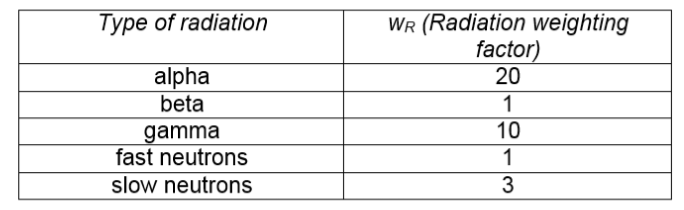
(ii) The risk of biological harm from radiation exposure depends on the absorbed dose and the type of radiation. Which other factor affects the risk of biological harm?