1. Calculate the acceleration of a car which takes 8s to increase its speed from 20ms-1 to 30ms-1.
2. Find the acceleration of a sprinter who reaches a speed of 8ms-1 after 2s of a race.
3. A group of students is using the apparatus shown to study the motion of a trolley.
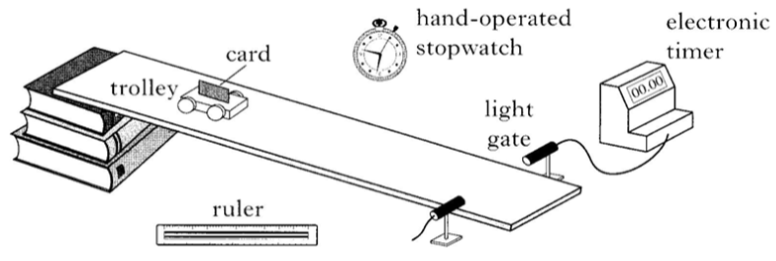
The trolley is released from rest at the top of the slope. The stopwatch measure the time taken for the trolley to reach the light gate.
a) Describe how to find the instantaneous speed of the trolley as it passes through the light gate.
You must state the measurements that are made and how they are used.
b) During one run, the instantaneous speed of the trolley through the light gate is calculated to be 0.8 metres per second. The stopwatch reading is 2.0 seconds.Calculate the acceleration of the trolley down the slope.
c) The light gate is moved closer to the top of the slope and the experiment is repeated. One student suggests that the value of acceleration obtained is more accurate because the reading on the stopwatch is less.Explain whether the student is correct or not.
4. A gun fires a bullet at 600ms-1. If it leaves the gun barrel 15ms after the trigger is pulled, find the acceleration of the bullet.
5. A lorry travelling at 30ms-1 takes 6s to come to a halt after the brakes are applied. Find its deceleration.
6. A jet plane moving at 450ms-1 accelerates at 18ms-2 for 7s. Calculate the final speed of the plane.
7. A driver presses the accelerator for 5s and reaches a speed of 30ms-1. If her acceleration was constant at 2ms-2. Calculate her initial speed.
8. During the Winter Olympics two skiing competitions are taking place. Both downhill racing and ski jumping are fast and dangerous sports which are very popular with spectators.

In down hill racing an electric clock automatically starts when the skier opens the start gate. The time for one competitor to complete a 3 km race is shown above.
(a) Calculate the average speed of the skier during this race.
At the finish line of the race a light gate is arranged so that the instantaneous speed of the skier can be measured.
(b) Using the information below calculate the final speed of the skier.
width of skier when crouched down (average ) = 60 cm
time on electronic clock = 0•02 s
(c) Calculate the acceleration of the skier during the race.
