(g = 9.8Nkg-¹)
- A ball of mass 1kg is thrown upwards at 10ms-¹.
(a) Calculate the initial kinetic energy of the ball.
(b) How much potential energy does the ball have at its highest point?
(c) Find the maximum height reached.
2.A slate of mass 2kg falls off a roof 45m up.
(a) Calculate the potential energy lost.
(b) Find the speed of the slate on impact.
3.A motorbike has 40kJ of kinetic energy at the moment the brakes are applied.
(a) If it takes 125m to come to a stop, find the average frictional force acting.
(b) Where has the kinetic energy gone?
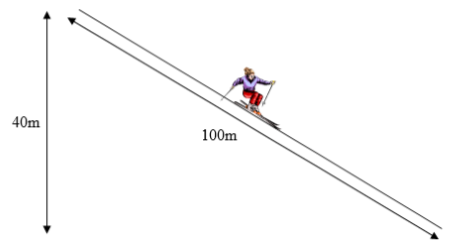
4.A skier of mass 50kg starts from rest at the top of a slope and is moving at 20ms-¹ by the time she reaches the bottom.
(a) Calculate her potential energy at the top of the slope.
(b) Calculate her kinetic energy at the bottom of the slope.
(c) Find the energy lost as heat due to friction.
(d) Calculate the average value of the frictional force.
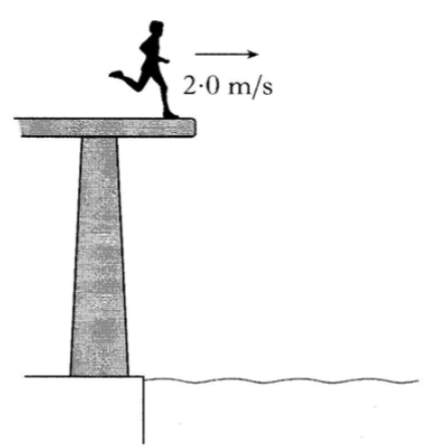
5۔ A student runs along a diving platform and leaves the platform horizontally with a speed of 2.0 m/s. The student lands in the water 0.3 s later. Air resistance is negligible.
(a)
(i) Calculate the horizontal distance travelled by the student before landing in the water.
(ii) The student has a vertical acceleration of 10 m/s2.
Calculate the vertical speed as the student enters the water.
(b)
Later the student runs off the end of the same platform with a horizontal speed of 3.0 m/s.
How long does the student take to reach the water this time?
Explain your answer.
(c)
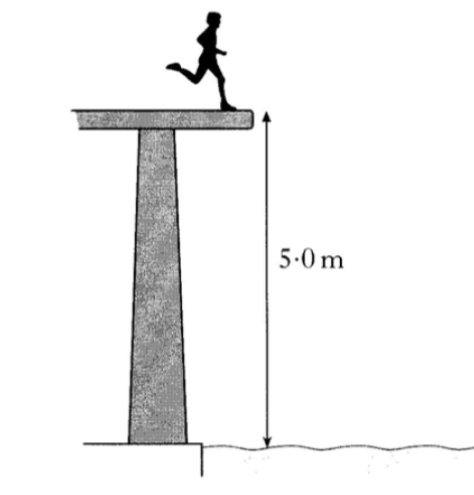
The student climbs from the water level to a higher platform. This platform is 5.0 m above the water. The student has a mass of 50 kg.
(i) Calculate the gain in gravitational potential energy of the student.
(ii) The student drops from the edge of the platform and lands in the water.
Calculate the vertical speed as the student enters the water.