 |
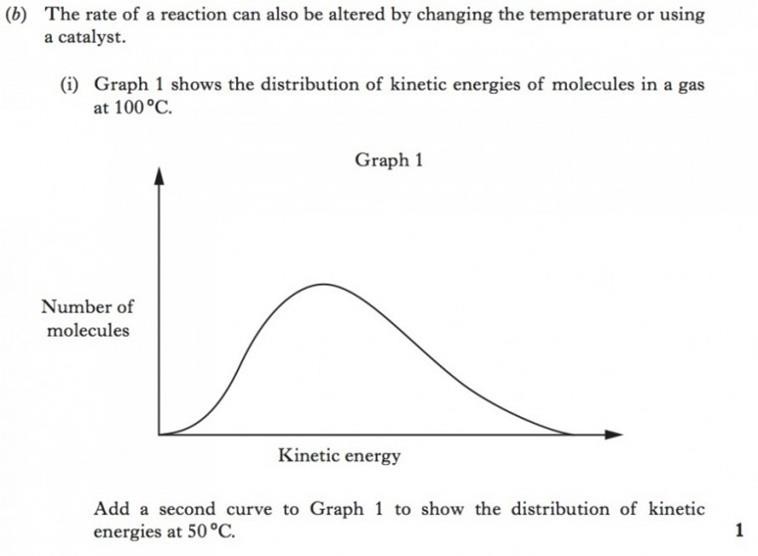 |
The particles (atoms or molecules) of solids liquids and gases are constantly in motion. The velocity with which a particle moves is a measure of its kinetic energy. The faster the speed, the greater the kinetic energy. For any substance, the particles making up the substance will be have a range of kinetic energy. For a collision between reactants, they must possess a minimum level of kinetic energy, called the activation energy (EA).
The kinetic energy of the particles can be shown on the graph below. For a given reaction a line can be added showing the activation energy (EA on the graph above). Those particles with kinetic energy greater than the activation energy have the potential to react if a collision occurs. (Not all collisions result in a reaction as the colliding particles must also collide with favourable collision geometry). |


