(f) Proteins are held in a three-dimensional shape — peptide bonds, folded polypeptide chains, hydrogen bonds, interactions between individual amino acids.
 |
Homework Sheets 1_6
All proteins are made by joining amino acids into long chains.  The chains are called polymers and the amino acids are the monomers. The amino acids are held together by peptide bonds, which are strong covalent bonds. When synthesised, the proten chain folds into a specific three dimensional shape, held in place by a variety of bonds, including weak hydrogen bonds. If these weak hydrgen bonds are broken, the protein’s shape will change and it will stop working properly. Hydrogen bonds are easily broken by a small rise in temperature, hence heating enzymes above around 40oC, often stops them functioning. This is called denaturation.
The chains are called polymers and the amino acids are the monomers. The amino acids are held together by peptide bonds, which are strong covalent bonds. When synthesised, the proten chain folds into a specific three dimensional shape, held in place by a variety of bonds, including weak hydrogen bonds. If these weak hydrgen bonds are broken, the protein’s shape will change and it will stop working properly. Hydrogen bonds are easily broken by a small rise in temperature, hence heating enzymes above around 40oC, often stops them functioning. This is called denaturation.
Hair is a protein called keratin. The curls in your hair are present because of the interactions between amino acids in the keratin chain. Wetting hair breaks some of the weak forces holding the hair in shape, which is why hair changes its shape when it is wet. As it drys, the forces are restored, returning the hair to its original shape.
Other interactions between amino acids also shape proteins and for a more permanent change to hair shape, some stronger, covalent bonds need to be broken. Covalent links such as disulphide bridges, which are bonds formed between two sulphur atoms are strong and more difficult to break. Perming solution breaks the disulphide bridges in keratin allowing the hair to be reshaped, before the disulphide bridges are made once again using the neutraliser solution.
Relaxers, which straighten hair also break disulphide bridges, but in this case, the disulphide bridges are not reformed.
 The shape is determined by the order in which the amino acids are put together – change the amino acids in the chain and the shape changes. The primary structure is the term used to describe this order of amino acids in the chain. There are other levels of protein structure which describe the shape of the protein. The order of amino acids is determined by the DNA base sequence of the gene that encodes the protein, a change in that base sequence is known as a mutation and will result in a malformed protein that most likely will function less well or not function at all -hence mutations are often harmful.
The shape is determined by the order in which the amino acids are put together – change the amino acids in the chain and the shape changes. The primary structure is the term used to describe this order of amino acids in the chain. There are other levels of protein structure which describe the shape of the protein. The order of amino acids is determined by the DNA base sequence of the gene that encodes the protein, a change in that base sequence is known as a mutation and will result in a malformed protein that most likely will function less well or not function at all -hence mutations are often harmful.
Some mutations can be useful however and are important in the process of evolution.
Start video at 10:40 to access the section on proteins.
Proteins have a variety of functions in cells. Your work in National 5 gave you a number of examples, including enzymes, antibodies, structural proteins, transport proteins and hormones.
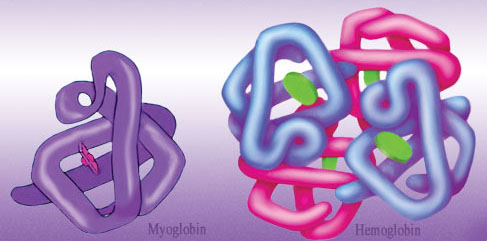
Proteins can be made of one polypeptide chain or a number of chains interacting. In addition, the polypeptide chains can be associated with non-protein molecules. Haemoglobin and myoglobin are both oxygen binding proteins which are proteins with an attached haem group (an organic molecule containing an iron atom – which gives the proteins their red colour). The haem group binds the oxygen.
Myoglobin is found in muscle (makes meat red) and consist of only a single polypepetide and associated haem group, whereas haemoglobin is found in blood and consists of 4 polypepdtide chains, each with an associated haem group.