Space and time
1. What is meant by an inertial frame of reference?
2. What is meant by a non-inertial frame of reference?
3. Which frame of reference applies to the theory of special relativity (studied in Higher Physics)?
4. At what range of speeds do the results obtained by the theory of special relativity agree with those of Newtonian mechanics?
5. How does the equivalence principle link the effects of gravity with acceleration?
6. In which part of an accelerating spacecraft does time pass more slowly?
7. Does time pass more quickly or more slowly at high altitude in a gravitational field?
8. How many dimensions are normally associated with space-time?
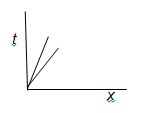
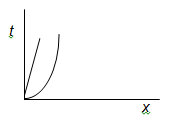
9. Two space-time diagrams are shown, with a worldline on each. Write down what each of the worldlines describes.
10. The space-time diagram shows two worldlines. Which worldline describes a faster speed?
(These speeds are much less than the speed of light.)
11. Explain the difference between these two worldlines on the space-time diagram.
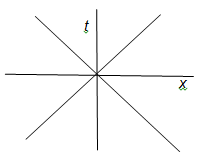
12. Explain what is meant by the term geodesic.
13. Copy the following space-time diagram.
Insert the following labels onto your diagram:
- the present
- the future
- the past
- v = c
- v ˂ c
- v ˃ c.
14. What effect does mass have on spacetime?
15. Describe two situations where a human body experiences the sensation of force.
16. How does general relativity interpret the cause of gravity?
17. Mercury’s orbit around the Sun could not be predicted accurately using classical mechanics. General relativity was able to predict Mercury’s orbit accurately. Investigate this using a suitable search engine and write a short paragraph summarising your results.
18. A star of mass 4.5 × 1031 kg collapses to form a black hole. Calculate the Schwarzschild radius of this black hole.
19. A star of mass equivalent to six solar masses collapses to form a black hole. Calculate the Schwarzschild radius of this black hole.
20. If our Sun collapsed to form a black hole, what would be the Schwarzschild radius of this black hole?
21. If our Earth collapsed to form a black hole, what would be the Schwarzschild radius of this black hole?
22. A star is approximately the same size as our Sun and has an average density of 2.2 × 103 kgm–3.
If this star collapsed to form a black hole, calculate the Schwarzschild radius of the black hole.