ROTATIONAL MOTION 1
- A rocket’s acceleration function is described by:
(a) Derive the velocity function, if at t = 0, the velocity is 10ms-1.
(b) Derive the displacement function if the initial displacement is 50m.
(c) Calculate the displacement of the rocket when t = 10s.
- A body moves with displacement function s = 4 + 12t – t3.
(a) When will it stop and reverse its direction of motion?
(b) Find its acceleration when t = 0.
(c) Find its acceleration at the time it reverses its direction.
(d) How can you tell from the position equation that the acceleration is not constant?
- If the Moon rotates about the Earth in a circular path of radius 3.85 x 108m, with a period of 27.3 days, find;
(a) Its angular velocity.
(b) Its speed relative to the Earth.
- A point on the rim of a train wheel of diameter 1.2m decelerates from 30ms-1 to 18ms-1 in 12s. Calculate;
(a) The angular deceleration
(b) The distance travelled by the train during this time.
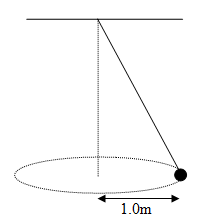
- A string 2.0m long is attached to a fixed point as shown.
A lead sphere of mass 75g is attached to the other end. If the sphere describes a horizontal circle of radius 1.0m with a steady speed, find;
(a) The tension in the string.
(b) The period of the pendulum.