Normalisation is the process of dividing a flat file database into smaller tables
In other words, normalisation removes the deletion, insertion and update anomalies from a database table.
A table which is in unnormalised form is a flat file table.
Example
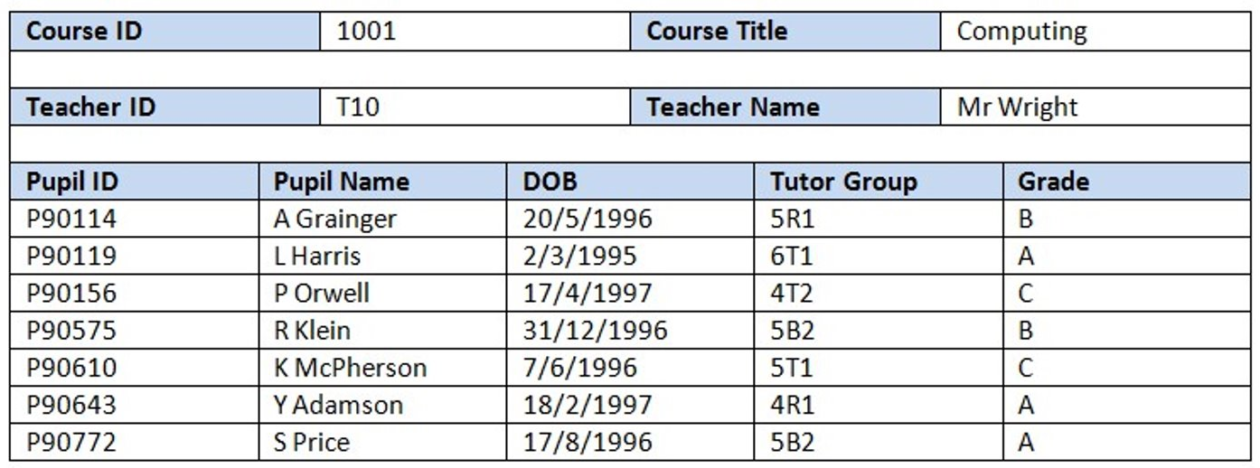
A school stores all of it’s course details in record cards with one record card for each course. A student may take several courses, and teachers may teach more than one course. A sample record card is shown below
Step 1: List the attributes
course_id
course_title
teacher_id
teacher_name
pupil_id
pupil_name
DOB
tutor_group
grade
Step 2: Identify the Primary key and underline it
course_id
course_title
teacher_id
teacher_name
pupil_id
pupil_name
DOB
tutor_group
grade
Step 3: Identify the repeating groups – using the primary key, decided if their is one value linked to the primary key or many values.
course_id
course_title 1
teacher_id 1
teacher_name 1
pupil_id m
pupil_name m
DOB m
tutor_group m
grade m
Linked to the Primary Key course_id, there is 1 course title and 1 teacher etc, but there are many pupil_id’s and pupil_names etc.
Step 4: Remove the repeating groups to a new entity – make sure you name both entity tables
Course (course_id
course_title
teacher_id
teacher_name )
Pupil (pupil_id
pupil_name
DOB
tutor_group
grade)
Step 5: Underline the new Primary key in the second entity and add the Foreign key to link both tables together and mark it with an asterisks *.
Course (course_id
course_title
teacher_id
teacher_name )
Pupil (pupil_id
pupil_name
DOB
tutor_group
grade
course_id*)