| 2. | Antibiotics act on | |
| |
A. | bacteria but not viruses |
| B. | viruses but not bacteria | |
| C. | viruses and bacteria | |
| D. | fungi and viruses | |
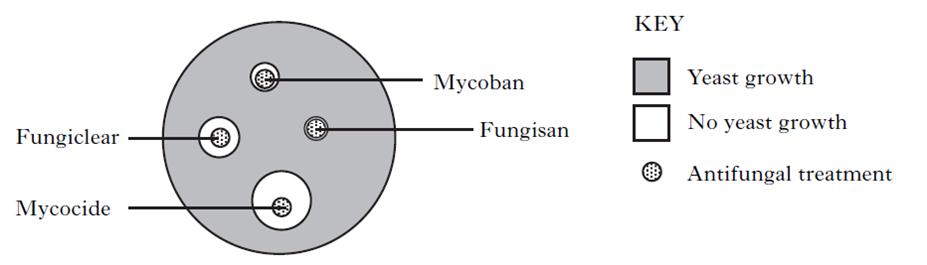
| 3. | An investigation was carried out into the effectiveness of four antifungal treatments on preventing the growth of yeast. The results are shown in the diagram below. Use the results to select the correct conclusion
|
||
| A. | All antifungal treatments are equally effective | ||
| B. | All antifungal treatments prevent growth of all yeasts | ||
| |
C. | Mycocide is most effective and Fungisan is least effective | |
| D. | Fungisan is most effective and Mycocide is least effective | ||
| 4. | Which line in the table below shows correctly the effect of antibiotics on the growth of bacteria and viruses?
|
||
| A. | A | ||
| B. | B | ||
| C. | C | ||
| |
D. | D | |
| 5. | Antibiotics are produced naturally by | |
| A. | yeast | |
| B. | bacteria | |
| |
C. | fungi |
| D. | viruses | |
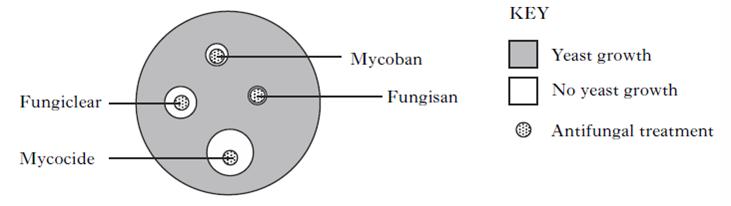
| 6. | An investigation was carried out into the effectiveness of four antifungal treatments on preventing the growth of yeast. The results are shown in the diagram below. Use the results to select the correct conclusion.
|
||
| A. | All antifungal treatments are equally effective. | ||
| B. | All antifungal treatments prevent growth of all yeasts. | ||
| |
C. | Mycocide is most effective and Fungisan is least effective. | |
| D. | Fungisan is most effective and Mycocide is least effective. | ||
| 7. | In the body’s first line defence mechanisms, friendly bacteria are useful because they | |
| A. | act as a barrier between pathogens and the body | |
| B. | kill bacteria and parasites that have been swallowed | |
| |
C. | stop other harmful bacteria from taking over |
| D. | flush out pathogens from the bladder area | |
| 8. | Tears form a part of the body’s first line defence mechanism. They | |
| |
A. | contain an enzyme that breaks down the cell wall of many bacteria. |
| B. | wash the bacteria out of our eyes | |
| C. | dissolve bacteria and drown them | |
| D. | show the bacteria we are sad, so they don’t infect us | |
| 9. | Which type of white blood cells ‘eats’ up pathogens? | |
| A. | Neutrophils | |
| B. | T helper cells | |
| |
C. | Macrophages |
| D. | B cells | |
| 10. | A pathogen is | |
| A. | a benificial bacteria | |
| B. | a doctor that cuts up dead bodies | |
| |
C. | a micro-organism which makes you sick |
| D. | the route by which micro-organisms enter the body | |
| 11. | One type of white blood cell remembers a pathogen so that your body can reaact to it more quickly. This blood cell is the | |
| |
A. | T-helper cell |
| B. | B cell | |
| C. | Macrophage | |
| D. | red blood cell | |
| 12. | A vaccine | |
| A. | contains parts of your immune system | |
| |
B. | contains weakened or killed pathogens |
| C. | treats infectious disease | |
| D. | must be given in the arm | |
| 13. | Vaccines | |
| A. | Don’t work against viruses | |
| B. | Only act against bacteria | |
| C. | Treat infections | |
| |
D. | Prevent infections |
| 14. | An antibody | |
| |
A. | are produced by B cells and “tag” pathogens for attack by the immune system |
| B. | are produced by T-helper cells and “tag” pathogens for attack by the immune system | |
| C. | are produced by B cells and stop pathogens entering the body | |
| D. | are produced by T-helper cells and stop pathogens entering the body | |
| 15. | The chemical used to test for the fitness for milk is | |
| A. | resazurin and it turns from purple to blue if lots of bacteria are present | |
| |
B. | resazurin and it turns from purple to white if lots of bacteria are present |
| C. | Methylene blue and it turns from white to purple if lots of bacteria are present | |
| D. | Methylene blue and it turns from purple to blue if lots of bacteria are present | |