| 1. 1 pt(s). |
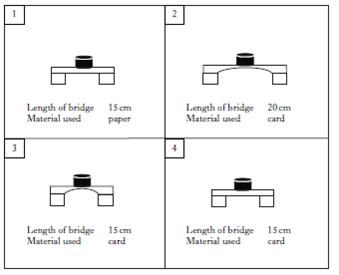
Janet investigated the strength of model bridges. She added weights to each bridge until the bridge collapsed. Janet wanted to find out how the length of a bridge affects its strength. Which two boxes show the experiments she should compare for a fair test?
|
||
| A. | 2 and 3 | ||
| B. | 2 and 4 | ||
| C. | 1 and 2 | ||
| D. | 1 and 3 | ||
| 2. 1 pt(s). |
Janet investigated the strength of model bridges. She added weights to each bridge until the bridge collapsed. Janet compared the experiments in boxes 1 and 4. What was she trying to find out?
|
||
| A. | How the length of the bridge affects the strength of the bridge | ||
| B. | How the material from which the bridge is made affects the strength of the bridge | ||
| C. | How the shape of the brdige affects the strength of the bridge | ||
| D. | If the bridge will fall down | ||
| 3. 1 pt(s). |
A road tanker delivers unleaded petrol, super-unleaded petrol and diesel to a filling station. The volume of unleaded petrol in the tanker is 6 600 litres. The volume of super-unleaded petrol is 1200 litres. Calculate the total volume of petrol.
|
||
| A. | 5400l | ||
| B. | 7800l | ||
| C. | 18600l | ||
| D. | 7920000l | ||
| 4. 1 pt(s). |
A road tanker delivers unleaded petrol, super-unleaded petrol and diesel to a filling station. The volume of unleaded petrol in the tanker is 6 600 litres. The volume of super-unleaded petrol is 1200 litres. The total volume of all three fuels in the tanker is 11000 litres. Calculate the volume of diesel.
|
||
| A. | 5400l | ||
| B. | 7800l | ||
| C. | 18800l | ||
| D. | 3200l | ||
| 5. 1 pt(s). |
A plumber fitted a 12 kg water tank in a house. He connected 4 copper pipes to the tank. Each pipe had a mass of 2 kg. What is the total mass of the water tank and the four pipes?
|
||
| A. | 12kg | ||
| B. | 14kg | ||
| C. | 20kg | ||
| D. | 56kg | ||
| 6. 1 pt(s). |
The wreck of a Spanish galleon was found by divers. The divers found five gold coins. The total mass of the five coins was 125 g. Calculate the mass of one coin.
|
||
| A. | 40g | ||
| B. | 25g | ||
| C. | 625g | ||
| D. | 125g | ||
| 7. 1 pt(s). |
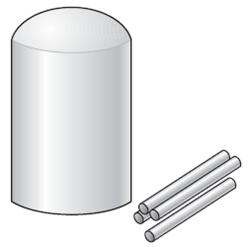
The diagram below shows 20 grams of two different materials, A and B, on a laboratory balance. Compared to material A, material B has a different
|
||
| A. | state | ||
| B. | mass | ||
| C. | shape | ||
| D. | density | ||
| 8. 1 pt(s). |
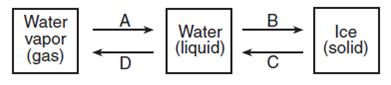
Examine the diagram below which represents four processes, labeled A, B, C, and D, that occur when water changes phase. Which process is represented by B?
|
||
| A. | condensing | ||
| B. | evaporating | ||
| C. | freezing | ||
| D. | melting | ||
| 9. 1 pt(s). |
Examine the diagram below which represents four processes, labeled A, B, C, and D, that occur when water changes state. Which two processes increase the motion of the molecules?
|
||
| A. | A and B | ||
| B. | B and C | ||
| C. | C and D | ||
| D. | D and A | ||
| 10. 1 pt(s). |
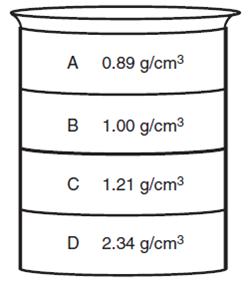
The diagram below shows a tall beaker with four different liquids and their densities. If a ball that has a density of 1.73 g/cm3 is placed in the beaker, where will the ball come to rest?
|
||
| A. | on top of liquid A | ||
| B. | between liquids B and C | ||
| C. | between liquids C and D | ||
| D. | on the bottom of the beaker | ||