| 1. 1 pt(s). |
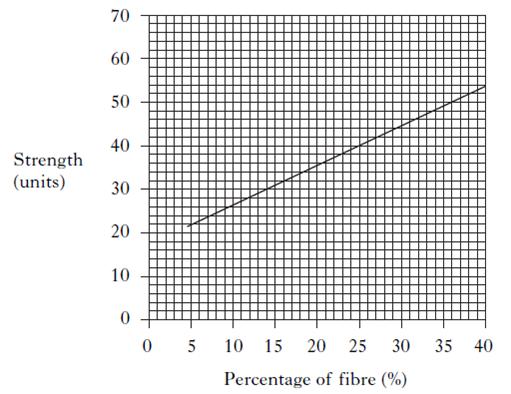
Plaster is mixed with fibre to make plasterboard. The graph below shows how the percentage of fibre in plasterboard affects its strength. What conclusion can be drawn from these results?
|
||
| A. | as the fibre content increases, the strength decreases | ||
| B. | as the strength increases, the fibre content decreases | ||
| C. | as the strength decreases, the fibre content increases | ||
| D. | as the fibre content increases, the strength increases | ||
| 2. 1 pt(s). |
Plaster is mixed with fibre to make plasterboard. The graph below shows how the percentage of fibre in plasterboard affects its strength. What is the strength of plasterboard that contains 25% fibre?
|
||
| A. | 9 units | ||
| B. | 40 units | ||
| C. | 35 units | ||
| D. | 45 units | ||
| 3. 1 pt(s). |
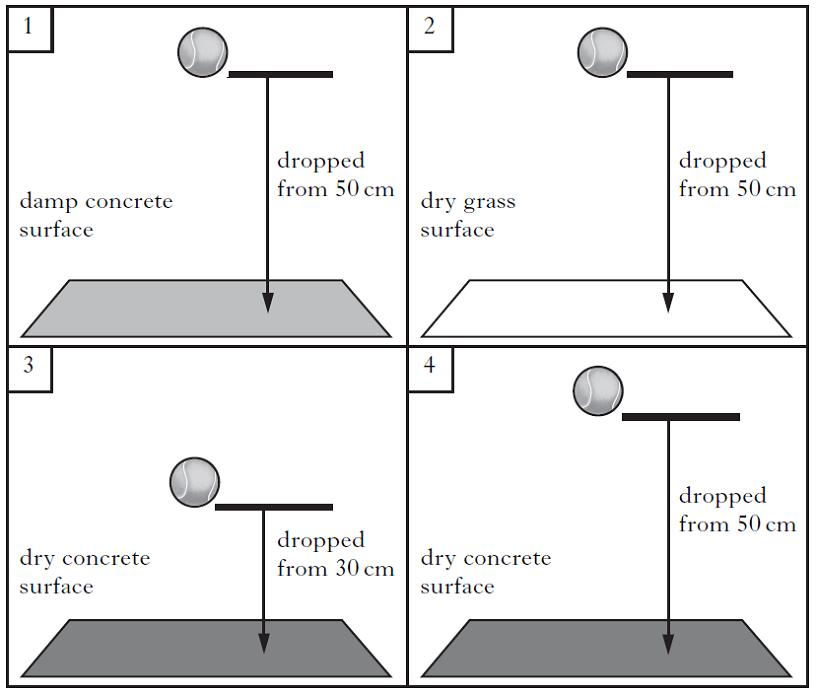
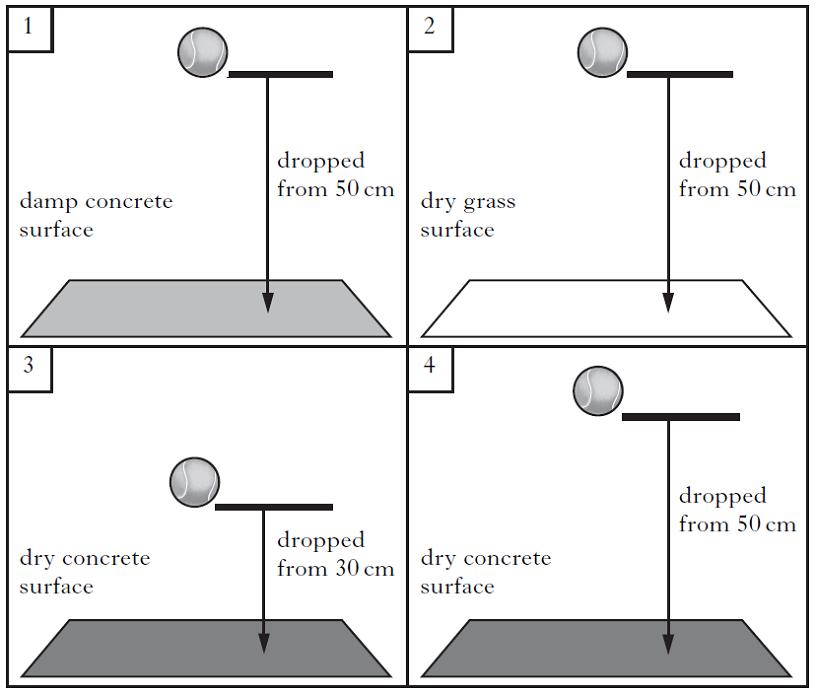
Marek investigated how high tennis balls bounce. For each experiment, he measured how high the tennis ball bounced after it hit the surface. Marek wanted to find out if the dampness of the surface affected how high the tennis ball bounced. Which two boxes show the experiments he should compare for a fair test?
|
||
| A. | 1 and 2 | ||
| B. | 1 and 3 | ||
| C. | 1 and 4 | ||
| D. | 3 and 4 | ||
| 4. 1 pt(s). |
Marek investigated how high tennis balls bounce. For each experiment, he measured how high the tennis ball bounced after it hit the surface. Marek wanted to find out if the dampness of the surface affected how high the tennis ball bounced. Which two boxes show the experiments he should compare for a fair test?
|
||
| A. | the effect of the height the ball is dropped from on the height of the bounce | ||
| B. | the effect of the material the surface is made from on the height of the bounce | ||
| C. | the effect of the shape of the ball on the height of the bounce | ||
| D. | the effect of grass on the height of the bounce | ||
| 5. 1 pt(s). |
Scott was investigating the flexibility of steel. He clamped a steel strip to a bench. He hung different masses from the end of the steel strip and measured its deflection. Using the results in the table below, predict the deflection if a 75g mass is hung on the steel strip.
|
||
| A. | 75mm | ||
| B. | 13mm | ||
| C. | 16mm | ||
| D. | 19mm | ||
| 6. 1 pt(s). |
Grant investigated the strength of a model bridge. When six 25 g and four 5 g masses were placed on the bridge, it collapsed. Calculate the total mass placed on the bridge.
|
||
| A. | 30g | ||
| B. | 40g | ||
| C. | 170g | ||
| D. | 250g | ||
| 7. 1 pt(s). |
When a mass is hung on a spring, it makes the spring stretch. Samuel set up the following experiments to investigate how springs stretch. Which two experiments would Samuel compare to find out if a copper springs stretches more than a steel spring?
|
||
| A. | B & E | ||
| B. | A & F | ||
| C. | B & E | ||
| D. | B & F | ||
| 8. 1 pt(s). |
When a mass is hung on a spring, it makes the spring stretch. Samuel set up the following experiments to investigate how springs stretch. Samuel compared experiments A, B and C. What was he trying to find out?
|
||
| A. | how the mass affects the stretch in the spring | ||
| B. | how the type of metal affects the stretch in the spring | ||
| C. | how the stretch in the spring affects the mass | ||
| D. | why springs are made of copper | ||
| 9. 1 pt(s). |
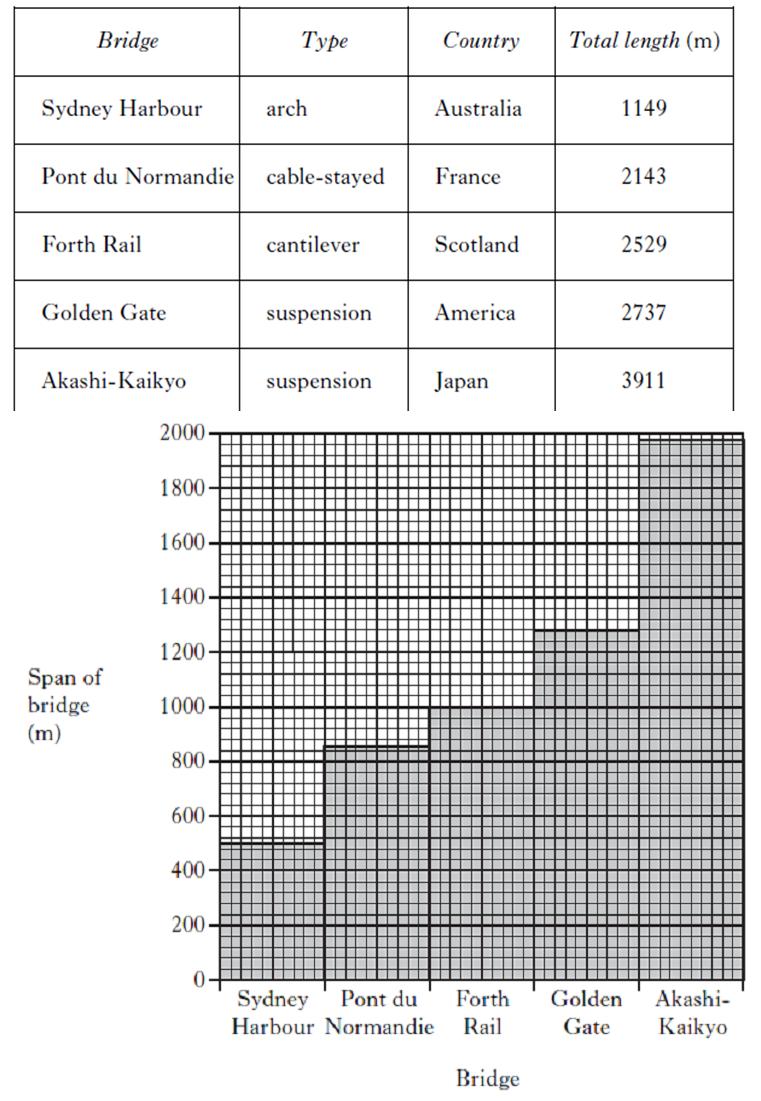
The table below shows information about some famous bridges. The span of a bridge is the distance between its support towers. The graph below shows the span of each bridge. In which country is the longest bridge?
|
||
| A. | Australia | ||
| B. | France | ||
| C. | Scotland | ||
| D. | America | ||
| E. | Japan | ||
| 10. 1 pt(s). |
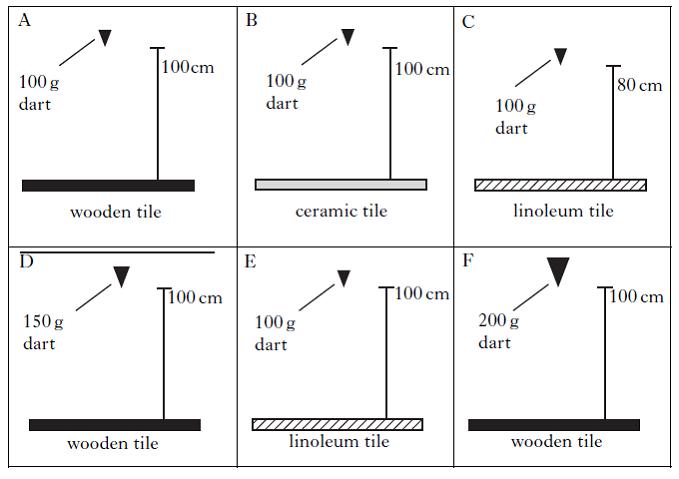
Jared was investigating the hardness of different floor tiles. He set up the following experiments. He dropped a steel dart on each tile and measured the size of the mark which was made. Which two experiments should Jared compare to find out if a wooden tile is harder than a linoleum tile?
|
||
| A. | A & E | ||
| B. | A & C | ||
| C. | A & B | ||
| D. | E & F | ||
| E. | C & F | ||