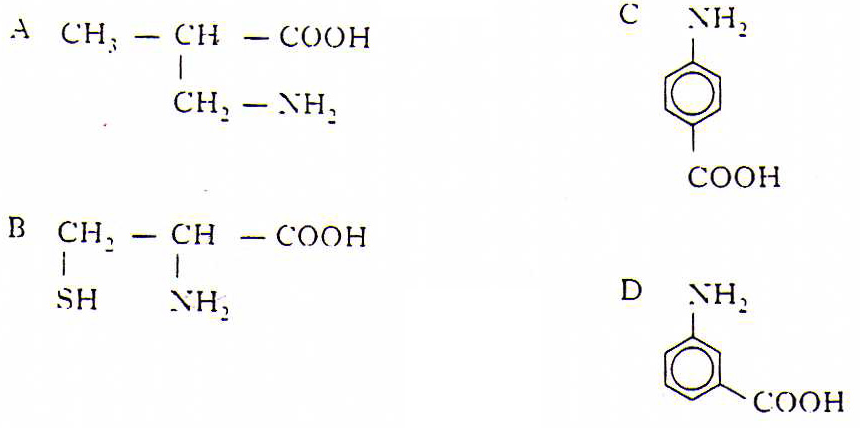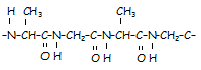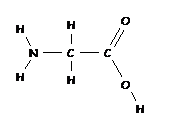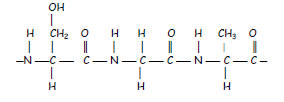A found in all plant proteins
B only made by the human body
C necessary for making all proteins
D needed by but not made in the body
2. A protein with the shape shown here is known as
A fibrous
B cyclic
C tubular
D globular
3. The catalytic action of an enzyme depends most on its molecular
A size
B shape
C mass
D formula
4. When an enzyme is denatured it
A functions more easily
B functions exactly the same
C functions more slowly
D stops functioning
5. An example of a protein with a fibrous nature is
A haemoglobin in the blood
B insulin from the pancreas
C keratin in the hair
D enzymes
6. What type of reaction is digestion?
A Hydrolysis
B Condensation
C Dehydration
D Hydration
7. The digestion of a protein molecule produces
A amino acids
B simple sugars
C amines
D enzymes
8. Which of the following types of bond are broken during the hydrolysis of proteins?
A C=O
B C-N
C C-H
D N-H
9. Describe two reasons why we need protein in our diet.
10. What four elements are present in proteins?
11. What is meant by the term essential amino acids?
12. When amino acids join together to form a protein molecule, what other chemical is produced?
13. Which of the following must contain nitrogen?
A an enzyme
B an oil
C a polyester
D a carbohydrate
14. On complete hydrolysis, a peptide produced 5 amino acids represented by the letters
P, Q, R, S and T. The following fragments were produced on partial hydrolysis.
![]()
Which one of the sequences below could be the correct one for the arrangement of amino acids
in the peptide?
A P-T-S-Q-R
B R-T-S-P-Q
C Q-P-T-S-R
D R-T-S-Q-P
15. Copy and complete the table giving details of proteins found in the human body.
16. Proteins can be denatured under acid conditions. During this denaturing, the protein molecule
A changes shape
B is dehydrated
C is neutralised
D is polymerised
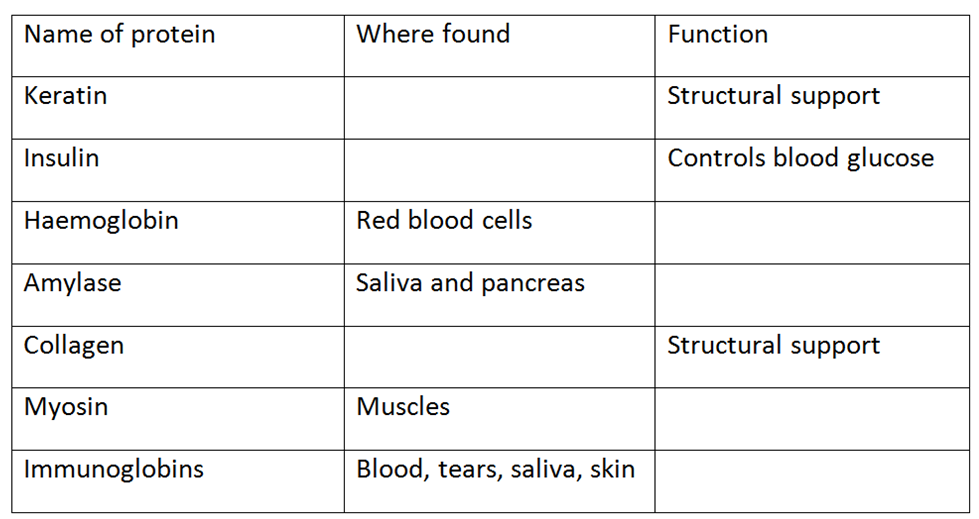
17. When two amino acids condense together, water is eliminated and a peptide link is formed.
Which of the following represents this process?
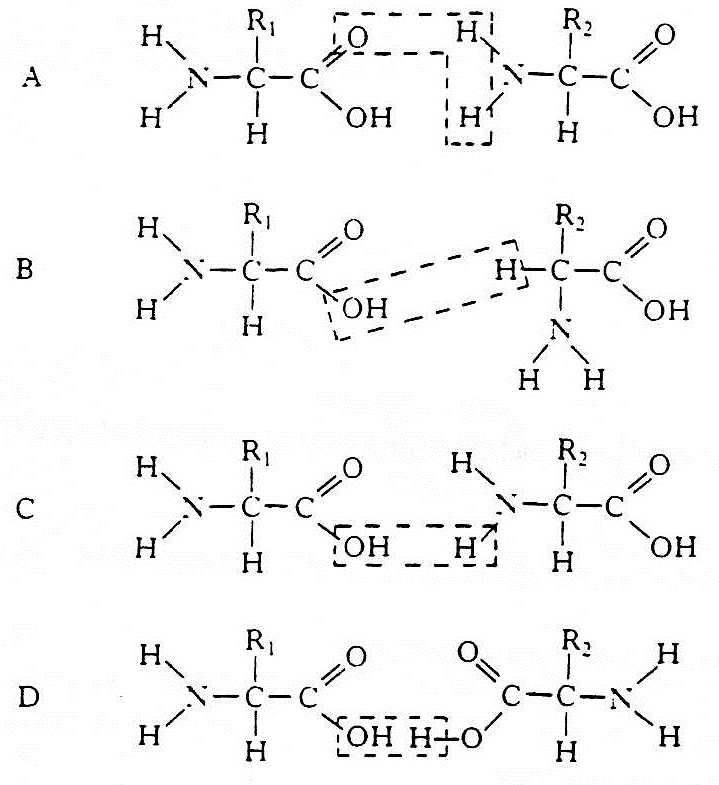
18. Some amino acids are called α(alpha) amino acids because the amino is on the carbon atom next to the acid group. Which of the following is an α(alpha) amino acid?
19. The following is part of a protein molecule (the bond angles are not correctly shown).
a) Draw the extended structural formula of two amino acids obtained on hydrolysis of this protein.
b) Draw an amide link.
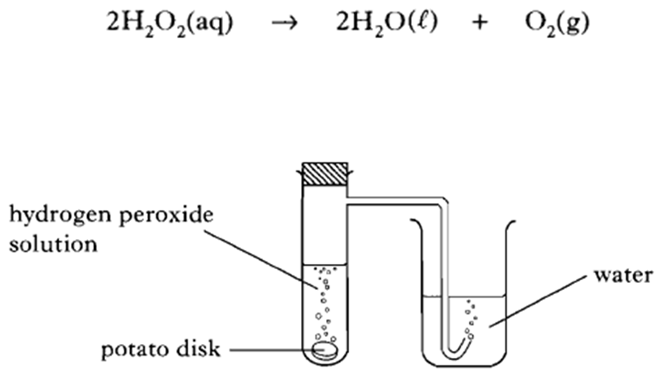
20. An enzyme found in potatoes can catalyse the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide.
The rate of the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide can be studied using the apparatus shown.
(a) Describe how this apparatus can be used to investigate the effect of temperature on the rate of decomposition of hydrogen peroxide.
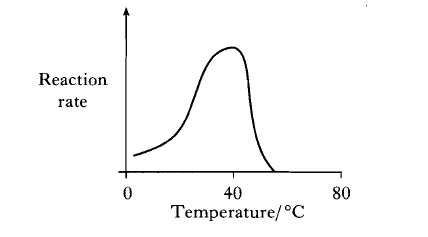
(b) The graph shows how the rate of the enzyme catalysed reaction changes with temperature.
Why does the reaction rate decrease above the optimum temperature of 40 “C?
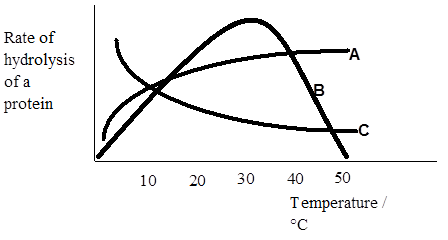
21. Examine the graphs below.
a) Which graph is likely to represent the results from a series of reactions using an enzyme? Explain your answer
b) To which family of compounds do enzymes belong?
c) Name the four elements which must be present in all enzyme molecules.
22. Glycine is an amino acid with the following structure.
a) Draw the structure of part of the polymer chain that would be formed when three glycine molecules polymerise.
b) What type of polymerisation process is taking place?
23.
a) Which type of natural substance has the structure shown?
b) Draw the structural formulae for the molecules formed when the fragment is hydrolysed.
c) To which class of substances do the hydrolysed products belong to?
d) Why can the molecule shown be called a polypeptide?
24. Peptides are molecules built up from amino acids: a dipeptide is formed from two amino acid molecules, a tripeptide from three amino acid molecules and a polypeptide from many amino acid molecules.
a) Draw the structural formula of the dipeptide formed from alanine and glutamic acid.
b) Name the other product of the reaction.
c) Name the type of reaction involved.
d) Go back to your drawing for answer a) and circle the peptide link.
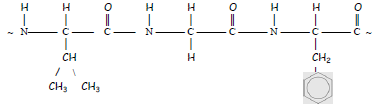
25. Imagine a protein molecule built up of the following repeated 500 times.
Calculate its molecular mass, remembering to add in an H and an OH to complete each end of the entire molecule.