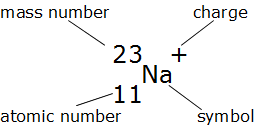| Number of Protons | This is the same as the atomic number – so in the example is 11 |
| Number of electrons | For atoms, this will be the same as the atomic number. |
| However ions are different, in that they have a charge. If the ion is positively charged, it means it has lost electrons(s). Consequently, the number of electrons will be calculated by subtracting the charge from the number of protons (atomic number – which never changes). | |
| In this example, the number electrons equals 10. | |
| If the ion is negatively charged, it means the atom has gained extra electrons. In this case the number of electrons will calculated by adding the charge to the number of protons (atomic number). | |
| Number of Neutrons | The mass of an atom is given by the number of neutrons (mass – 1 amu) plus the number of protons (mass – 1 amu). |
| Consequently, the number of neutrons can be calculated by subtracting the atomic number (number of protons) from the mass number. | |
| In this example, the number of neutrons equals 12. | |