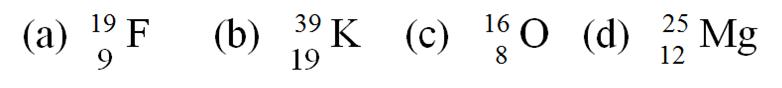Part 3 – Structure of the Atom and the Periodic Table
1. Draw a labelled diagram of the atom to show the nucleus, protons, electrons and neutrons.
2. Copy and complete the following table to show the masses and charges of the sub-atomic particles.
3. State the charge of the nucleus.
4. Explain why atoms are neutral.
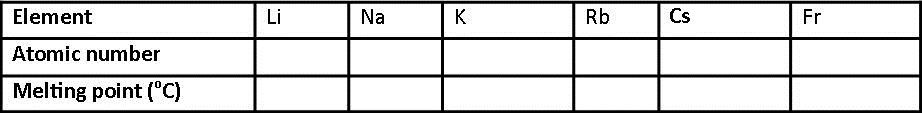
5. Use your data booklet to copy and complete the following table.
(a) What is the relationship between atomic number and melting point for the group 1 elements?
(b) In terms of electron, why do these elements have similar chemical properties?
(c) What name is given to this group of elements?
6. State the number of protons, electrons and neutrons in the following atoms.
7. Copy and complete the following table

8.(a) Name the elements with the following electron arrangements:
(b) From the list above name the element that is a member of:
![]()
9. Write nuclide notation for the following atoms:
(a) An oxygen atom with 10 neutrons
(b) An atom with atomic number 6 and 7 neutrons
(c) An atom with 17 protons and 20 neutrons
(d) An atom of hydrogen, mass number 3.
10. Two different kinds of magnesium atom are shown below.

(a) What word is used to describe these types of atoms?
(b) Explain why they can be regarded as atoms of the same element?
(c) The relative atomic mass of magnesium is 24.3. What does this tell you about the relative amounts of each atom?
11. An atom has atomic number 23 and mass number 51. The number of electrons is
12. An atom is neutral because
A the number of protons equals the number of neutrons
B the number of electrons equals the number of protons
C the number of electrons equals the number of protons plus neutrons
D the number of neutrons equals the number of protons plus electrons
13. Which of the following is the electron arrangement of a metal?
14. Different isotopes of the same element have identical
15. Copy and complete the table to show the particles present in the following atoms
and ions.