1. Oxygen consumption is often used to measure the intensity of exercise. VO2max is the
maximum rate at which someone can take up and use oxygen. Graph 1 shows the
VO2max of office workers, and various professional sportsmen and sportswomen.
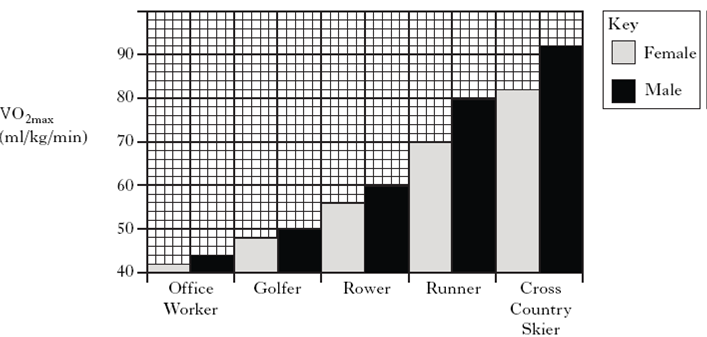
a) i) What is the difference between the VO2max of a male cross-country skier and a male
office worker?
ii) Cross-country skiing is a very energy demanding sport. What is the advantage to a
cross-country skier of having a high VO2max?
b) Calculate the oxygen uptake, during a three minute race, of a female rower who
weighs 85 kg. Assume that she has maximum oxygen uptake throughout the race.
c) The graph shows that, on average, men have higher maximum oxygen uptakes than
women. Suggest a reason for this difference.
Tests which determine the VO2max of individuals use the relationship between heart
rate and oxygen uptake. The maximum oxygen uptake occurs when an individual’s heart
is beating at its maximum rate.
Graph 2 shows measurements of heart rate and oxygen uptake for a professional
sportsman and an office worker, who are both 24 years old. The measurements were
taken as speed was gradually increased on a treadmill.
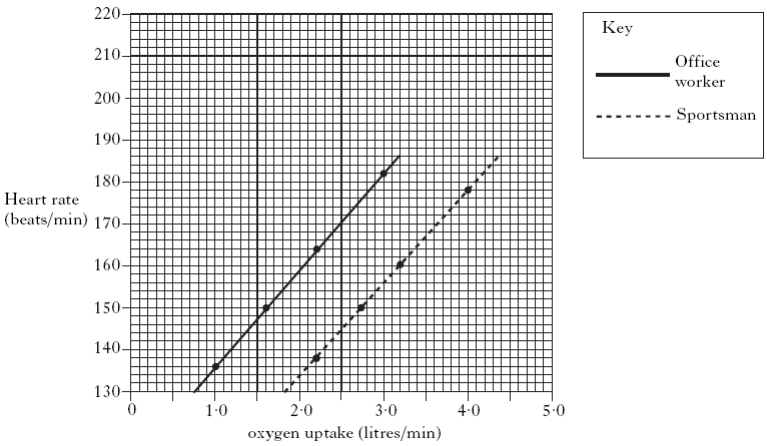
d) i) An individual’s maximum heart rate can be calculated by subtracting their age from
220. Calculate the maximum heart rate of the office worker in beats/min.
ii) Use the graph to predict the maximum oxygen uptake of the office worker in litres/min.
iii) The sportsman weighed 60 kg. Use the information in graphs 1 and 2 to determine his
sport.
2. An investigation was carried out to find out how a cyclist’s metabolism changed while
he pedalled at increasing speed. The cyclist’s heart rate, fat and carbohydrate
consumption were measured at different power outputs. The graph below shows the
results of the investigation.
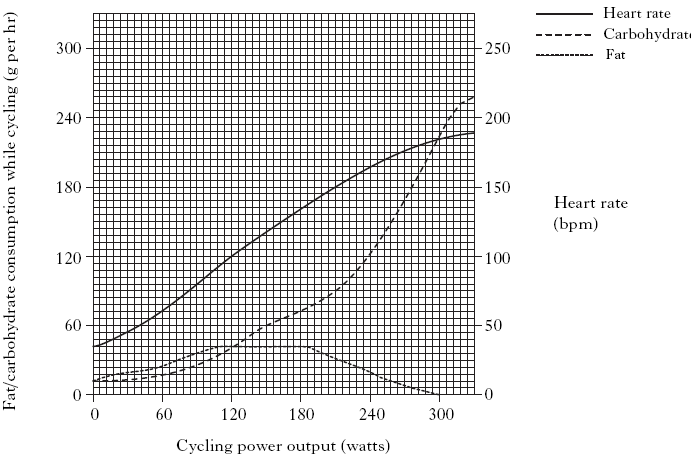
a) What is the heart rate (bpm) of the cyclist when his power output is 90 watts?
b) Compare the consumption of fat and carbohydrate as cycling power increases.
Quote data from the graph in your answer.
c) Cyclists often use heart-rate monitors in training. A cyclist wishes to maintain his fat
consumption at its maximum and, at the same time, limit his carbohydrate consumption.
At what heart rate (bpm) should he cycle?
d) The cyclist raced for 4 hours at a power output of 210 watts. During that time he
consumed 100 g of carbohydrate in a drink. Assuming he started with a carbohydrate
store of 500 g, how much carbohydrate (g) would he be left with at the end of the race?
e) This investigation used fat and carbohydrate consumption to measure metabolism.
Name one other measurement which can be taken to calculate metabolic rate.
3. The diagrams below represent the structure of three different animal’s hearts.
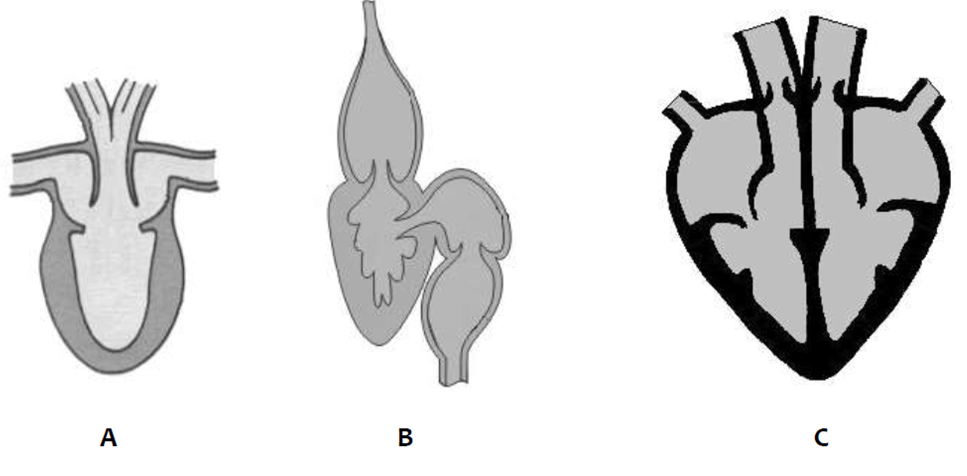
State which heart (A, B or C) could be an amphibian’s and explain your choice.
