| 1. | In rabbits, black fur (B) is dominant to brown fur (b). What is the genotype of a black rabbit? | |
| A. | BB | |
| B. | Bb | |
| C. | bb | |
| D. | Either BB or Bb | |
| 2. | In rabbits, black fur (B) is dominant to brown fur (b). The black and brown versions of the gene are called: | |
| A. | mutations | |
| B. | alleles | |
| C. | chromosomes | |
| D. | gametes | |
| E. | clones | |
| 3. | In rabbits, black fur (B) is dominant to brown fur (b). If two heterozygous black rabbits mate, how many of their offspring are likely to be black? | |
| A. | None of them | |
| B. | 1 out of 2 | |
| C. | 1 out of 4 | |
| D. | 3 out of 4 | |
| E. | All of them | |
| 4. | In rabbits, black fur (B) is dominant to brown fur (b). If a heterozygous black rabbit mates with a homozygous black rabbit, how many of their offspring are likely to be black? | |
| A. | None of them | |
| B. | 1 out of 2 | |
| C. | 1 out of 4 | |
| D. | 3 out of 4 | |
| E. | All of them | |
| 5. | In rabbits, black fur (B) is dominant to brown fur (b). What is the phenotype of a rabbit with the genotype bb? | |
| A. | Black | |
| B. | Brown | |
| C. | Homozygous | |
| D. | Heterozygous | |
| E. | Mutant | |
| 6. | In rabbits, black fur (B) is dominant to brown fur (b). If a group of black rabbits is ‘true breeding’, what does this mean? | |
| A. | All of their descendants will be black | |
| B. | Some of their descendants will be brown | |
| C. | All of their ancestors were black | |
| D. | Some of their ancestors were brown | |
| 7. | In corn on the cob, yellow seed (G) is dominant to purple seed (g). A cob was examined and found to contain 125 yellow seeds and 124 purple seeds. The genotypes of the parents that produced this cob were | |
| A. | GG × gg | |
| B. | Gg × gg | |
| C. | gg × gg | |
| D. | Gg × Gg | |
| 8. | A hairy stemmed pea plant is crossed with a smooth stemmed pea plant. All the F1 plants had hairy stems. The genotype of the F1 plants was | |
| A. | heterozygous | |
| B. | homozygous | |
| C. | dominant | |
| D. | recessive | |
| 9. | A species can be defined as a group of organisms which | |
| A. | breed together to produce fertile offspring | |
| B. | have the same phenotypes | |
| C. | contain the same number of chromosomes | |
| D. | contain identical genetic material | |
| 10. | In humans, the allele for blood group A is dominant to the allele for blood group O. Two parents both have blood group A. Their child has blood group O. What is the best explanation for this pattern of inheritance? | |
| A. | The child has inherited the blood group directly from a grandparent | |
| B. | The parents are homozygous for the blood group alleles | |
| C. | The parents are heterozygous for the blood group alleles | |
| D. | There has been a mutation in the blood group alleles | |
| 11. | A hairy stemmed pea plant was crossed with a smooth stemmed pea plant and all of the F1 had hairy stems. The genotype of the hairy stemmed parent plant is | |
| A. | heterozygous dominant | |
| B. | heterozygous recessive | |
| C. | homozygous recessive | |
| D. | homozygous dominant | |
| 12. | In gerbils, agouti coat colour is dominant to white. Some heterozygous gerbils were allowed to interbreed and 56 offspring were produced. What would be the expected number of agouti gerbils? | |
| A. | 14 | |
| B. | 28 | |
| C. | 56 | |
| D. | 42 | |
| 13. | In the fruit fly Drosophila, the allele for normal wings is dominant to the allele for short wings. A normal winged fly was crossed with a short winged fly and all the F1 offspring had normal wings. If these F1 offspring were to mate with each other, what percentage of the F2 offspring would be expected to have normal wings? | |
| A. | 25% | |
| B. | 50% | |
| C. | 75% | |
| D. | 100% | |
| 14. | In a breed of dog, the alleles for white coat colour and black coat colour are co-dominant. A cross was performed between two heterozygous dogs. Which line in the table below shows the numbers of different phenotypes and genotypes which are possible in the offspring? | |
| A. | 1 phenotype; 3 genotypes | |
| B. | 1 phenotype; 3 genotypes | |
| C. | 3 phenotype; 2 genotypes | |
| D. | 3 phenotype; 3 genotypes | |
| 15. | A snapdragon flower produces an average of 320 seeds. A pansy produces an average of 400 seeds. What is the ratio of the seeds produced by the snapdragon compared to that of the pansy? | |
| A. | 32: 40 | |
| B. | 320: 400 | |
| C. | 8: 10 | |
| D. | 4: 5 | |
| 16. | A section of chromosome which carries a separate piece of genetic information is called a | |
| A. | protein | |
| B. | gene | |
| C. | base | |
| D. | nucleus | |
| 17. | The function of DNA is to | |
| A. | act as an enzyme | |
| B. | release energy in cells | |
| C. | carry genetic instructions | |
| D. | form cell structure | |
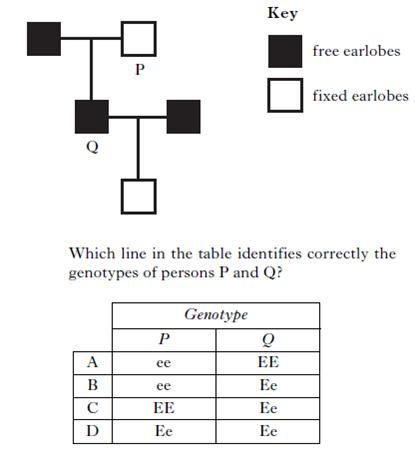
| 18. | In humans, the allele for free earlobes (E) is dominant to the allele for fixed earlobes (e). The diagram below shows the inheritance of this characteristic.
|
||
| A. | A | ||
| B. | B | ||
| C. | C | ||
| D. | D | ||
| 19. | A hairy stemmed pea plant was crossed with a smooth stemmed pea plant and all of the F1 had hairy stems. The genotype of the hairy stemmed parent plant is | |
| A. | heterozygous dominant | |
| B. | heterozygous recessive | |
| C. | homozygous recessive | |
| D. | homozygous dominant | |
| 20. | Gregor Mendel proposed that traits observed in pea plants resulted from a combination of “factors” inherited from each parent. His description of these “factors” can be considered the first scientific definition of the role of — | |
| A. | ribosomes | |
| B. | meiosis | |
| C. | genes | |
| D. | cell nuclei | |