| 1. | A dominant allele | |
| A. | is bigger than a recessive allele | |
| B. | is usually represented by a small letter | |
| C. | always shows up in the phenotype | |
| D. | is masked by a recessive allele | |
| 2. | A recessive allele | |
| A. | shows up in a homozygous individual | |
| B. | never shows up in the phenotype | |
| C. | always shows up in the phenotype | |
| D. | shows up in a heterozygous individual | |
| 3. | The genotype of an organism | |
| A. | describes its appearance | |
| B. | is written in words | |
| C. | is determined by its phenotype | |
| D. | is the combination of its alleles | |
| 4. | The phenotype of an organism is | |
| A. | a combination of alleles | |
| B. | masked by the genotype | |
| C. | represented by letters | |
| D. | what it looks like | |
| 5. | In a homozygous organism | |
| A. | only dominanat alleles are present | |
| B. | both alleles are identical | |
| C. | only recessive alleles are present | |
| D. | both alleles are different | |
| 6. | In a heterozygous organism, the alleles present are | |
| A. | both the same | |
| B. | different | |
| C. | both dominant | |
| D. | both recessive | |
| 7. | In mice, black coat (B) is dominant to white coat (b). A mouse with genotype bb is | |
| A. | homozygous dominant | |
| B. | black | |
| C. | homozygous recessive | |
| D. | heterozygous | |
| 8. | In mice, black coat (B) is dominant to white coat (b). A mouse with genotype Bb is | |
| A. | black | |
| B. | white | |
| C. | grey | |
| D. | spotted | |
| 9. | In mice, black coat (B) is dominant to white coat (b). A mouse with genotype Bb | |
| A. | is white | |
| B. | is homozygous recessive | |
| C. | is homozygous dominant | |
| D. | is heterozygous | |
| 10. | A monohybrid cross follows the inheritance of | |
| A. | one chracteristic | |
| B. | two characteristics | |
| C. | three characteristics | |
| D. | four characteristics | |
| 11. | All true breeding organisms | |
| A. | have the same characteristics | |
| B. | produce gametes with different characteristics | |
| C. | always pass on the same characteristic to their offspring | |
| D. | pass on different characteristics to their offspring | |
| 12. | A true breeding organism is always | |
| A. | homozygous | |
| B. | heterozygous | |
| C. | dominant | |
| D. | recessive | |
| 13. | What is the correct order of generations in a cross? | |
| A. | P, F2, F1 | |
| B. | F1, F2, P | |
| C. | P, F1, F2 | |
| D. | F2, F1, P | |
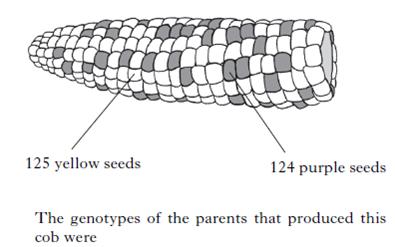
| 14. | In corn on the cob, yellow seed (G) is dominant to purple seed (g). The cob shown below shows some yellow and some purple seeds. The seeds have been counted.
|
||
| A. | GG × gg | ||
| B. | Gg × gg | ||
| C. | gg × gg | ||
| D. | Gg × Gg | ||
| 15. | A hairy stemmed pea plant is crossed with a smooth stemmed pea plant. All the F1 plants had hairy stems. The genotype of the F1 plants was | |
| A. | heterozygous | |
| B. | homozygous | |
| C. | dominant | |
| D. | recessive | |
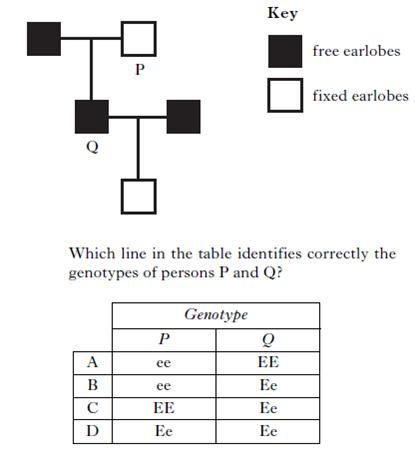
| 16. | In humans, the allele for free earlobes (E) is dominant to the allele for fixed earlobes (e). The diagram below shows the inheritance of this characteristic.
|
||
| A. | A | ||
| B. | B | ||
| C. | C | ||
| D. | D | ||
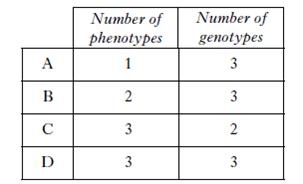
| 17. | In a breed of dog, the alleles for white coat colour and black coat colour are co-dominant. A cross was performed between two heterozygous dogs. Which line in the table below shows the numbers of different phenotypes and genotypes which are possible in the offspring?
|
||
| A. | A | ||
| B. | B | ||
| C. | C | ||
| D. | D | ||
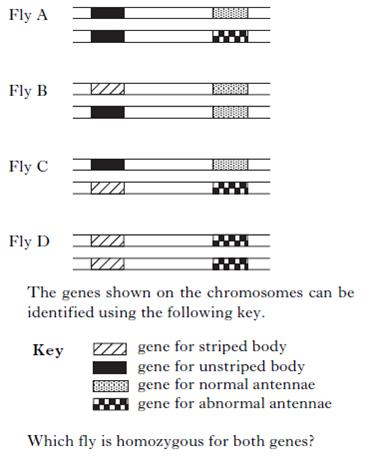
| 18. | The diagram below shows the same sections of matching chromosomes found in four fruit flies, A, B, C and D.
|
||
| A. | A | ||
| B. | B | ||
| C. | C | ||
| D. | D | ||
| 19. | In tomato plants, the allele for red fruit is dominant to that for yellow fruit. If a heterozygous tomato plant is crossed with a tomato plant which produces yellow fruit, the expected phenotype ratio of the offspring would be | |
| A. | 3 red: 1 yellow | |
| B. | 1 red: 3 yellow | |
| C. | 1 red; 2 yellow | |
| D. | 1 red: 1 yellow | |
| 20. | All of these can be inherited by people EXCEPT — | |
| A. | height | |
| B. | eye color | |
| C. | blood type | |
| D. | language | |