| 1. | In pea plants, the allele for pink flower petals (P) is dominant to that for white flowers (p). A true breeding pink-flowered plant is crossed with a true breeding white flowered plant and the plants of the F1 generation are self-crossed. In the F1 generation | |
| A. | all of the plants will have white flowers | |
| B. | there will be more pink flowered plants than white flowered plants | |
| C. | there will be an equal number of pink flowered and white flowered plants | |
| D. | all of the plants will have pink flowers | |
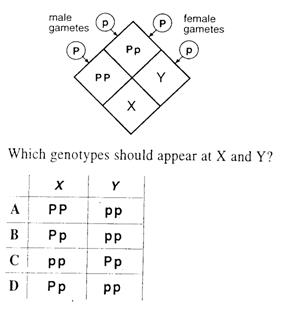
| 2. | In pea plants, the allele for pink flower petals (P) is dominant to that for white flowers (p). A true breeding pink-flowered plant is crossed with a true breeding white flowered plant and the plants of the F[sub]1[/sub] generation are self-crossed. The Punnett square shows the genotypes arising in the F2 generation of this cross
|
||
| A. | A | ||
| B. | B | ||
| C. | C | ||
| D. | D | ||
| 3. | In pea plants, the allele for pink flower petals (P) is dominant to that for white flowers (p). A true breeding pink-flowered plant is crossed with a true breeding white flowered plant and the plants of the F1 generation are self-crossed. In the F2 generation what would be the phenotype ratio. | |
| A. | 1 pink: 3 white | |
| B. | 3 pink: 1 white | |
| C. | 2 pink: 2 white | |
| D. | 4 pink: 1 white | |
| 4. | A test cross is used to find the | |
| A. | genotype of an individual showing a dominant characteristic | |
| B. | phenotype of an individual with an unknown phenotype | |
| C. | genotype of an individual showing a recessive characteristic | |
| D. | the phenotype of an individual with a known genotype | |
| 5. | In mice, the allele for black coat (B) is dominant to that for white coat (b). A mouse with a black coat can be | |
| A. | either homozygous dominant or homozygous recessive | |
| B. | either homozygous dominant or heterozygous | |
| C. | either homozygous recessive or heterozygous | |
| D. | only homozygous dominant | |
| 6. | In mice, the allele for black coat (B) is dominant to that for white coat (b). A test cross was carried out to determine the genotype of a mouse with a black coat. A possible result of this test cross might be | |
| A. | all offspring white | |
| B. | all offspring black | |
| C. | all offspring bb | |
| D. | all offspring recessive | |
| 7. | In mice, the allele for black coat (B) is dominant to that for white coat (b). A mouse with a black coat can be | |
| A. | either homozygous dominant or homozygous recessive | |
| B. | either homozygous dominant or heterozygous | |
| C. | either homozygous recessive or heterozygous | |
| D. | only homozygous dominant | |
| 8. | In pea flowers, the allele for red petal colour (R) is dominant to that for white petal colour (r). A cross between two plants produced offspring with a phenotype ratio of 3 red petals: 1 white petals. What were the genotypes of the parents? | |
| A. | RR x rr | |
| B. | Rr x rr | |
| C. | Rr x RR | |
| D. | Rr x Rr | |
| 9. | In pea flowers, the allele for red petal colour (R) is dominant to that for white petal colour (r). If the cross RR x Rr is carried out, what will be the phenotype ratio of the offspring | |
| A. | 3 red petals: 1 white petals | |
| B. | All red petals | |
| C. | 1 red petals : 1 white petals | |
| D. | All white petals | |
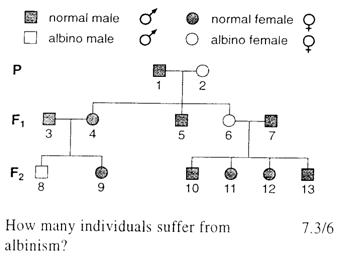
| 10. | The family tree shows the inheritance of albinism in a family. It is a recessive condition involving lack of pigment in the skin, eyes and hair.
|
||
| A. | 2 | ||
| B. | 3 | ||
| C. | 4 | ||
| D. | 9 | ||
| 11. | The family tree shows the inheritance of albinism in a family. It is a recessive condition involving lack of pigment in the skin, eyes and hair. Individual 8 has
|
||
| A. | two normal alleles | ||
| B. | the same alleles as his father | ||
| C. | one normal and one recessive allele | ||
| D. | two recessive alleles | ||
| 12. | The family tree shows the inheritance of albinism in a family. It is a recessive condition involving lack of pigment in the skin, eyes and hair. The genotypes of which individuals can be identified from their phenotype? | |
| A. | 2, 6, 8 | |
| B. | 2, 3, 11 | |
| C. | 5, 7, 9 | |
| D. | 2, 1, 12 | |
| 13. | Achoo syndrome is a dominant characteristic in humans which causes the sufferer to sneeze when they look at light. A woman who is homozygous for Achoo syndrome and a man who is unaffected have children. What proportion of their children would be expected to have Achoo syndrome? | |
| A. | 0% | |
| B. | 25% | |
| C. | 50% | |
| D. | 100% | |
| 14. | A pure-breeding male black mouse is mated with a female brown mouse and they produce a litter of 12. The allele for black fur is dominant to the allele to brown fur. What is the expected distribution of colour and sex in their litter? | |
| A. | 6 brown females and 6 black males | |
| B. | 9 black and 3 brown, all male | |
| C. | 6 black males and 6 black females | |
| D. | 12 black males | |
| 15. | A male heterozygous black mouse is mated with a female heterozygous black mouse and the litter consists of 12 pups. B is the allele for the black colour. The allele for brown colour is b. The dominant allele is B. Which of these ratios is closest to the expected ratio for the distribution of colour among the offspring? | |
| A. | All black | |
| B. | 6 black and 6 brown | |
| C. | 4 black and eight brown | |
| D. | 8 black and 4 brown | |
| 16. | In dogs, L is the allele for long hair and l is the allele for short hair. B is the allele for black hair and b is the allele for white hair. S is the allele for straight hair and s is the allele for curly hair. What will be the phenotype for a small dog with the genotype LLBbss? | |
| A. | Long, white, straight fur | |
| B. | Long, black, curly fur | |
| C. | Long, white, curly fur | |
| D. | Short, black, straight fur | |
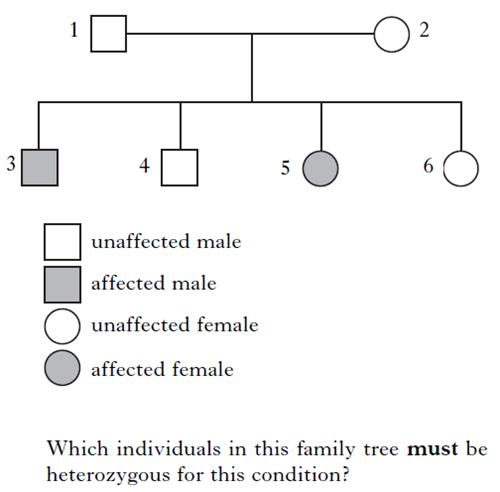
| 17. | Cystic fibrosis is an inherited condition caused by a recessive allele. The diagram below shows a family tree with affected individuals.
|
||
| A. | 3 and 5 | ||
| B. | 4 and 6 | ||
| C. | 1 and 2 | ||
| D. | 2 and 6 | ||
| 18. | Cystic fibrosis is a genetic condition caused by a single gene mutation. A child is born with cystic fibrosis despite neither parent having the condition. The parents are going to have a second child. What is the chance that the second child will have cystic fibrosis? | |
| A. | 75% | |
| B. | 67% | |
| C. | 50% | |
| D. | 25% | |
| 19. | In rabbits, black fur (B) is dominant to brown fur (b). If a true-breeding black rabbit mates with a brown rabbit, their offspring will be: | |
| A. | Homozygous and black | |
| B. | Heterozygous and black | |
| C. | Homozygous and brown | |
| D. | Heterozygous and brown | |
| 20. | In humans, the allele for blood group A is dominant to the allele for blood group O. Two parents both have blood group A. Their child has blood group O. What is the best explanation for this pattern of inheritance? | |
| A. | The child has inherited the blood group directly from a grandparent | |
| B. | The parents are homozygous for the blood group alleles | |
| C. | The parents are heterozygous for the blood group alleles | |
| D. | There has been a mutation in the blood group alleles | |