| 1. | A pyramid of energy shows | |
| A. | what happens to the solar energy entering a food chain | |
| B. | how the organisms in a food chain use energy | |
| C. | the quantity of energy at each stage in a food chain | |
| D. | how energy is passed from one food chain to another | |
| 2. | As energy flows along a food chain it becomes | |
| A. | less because some is used for growth by the organisms | |
| B. | less because some is lost by the organisms as movement and heat | |
| C. | more because some is gained as movement and heat | |
| D. | more because some is gained as organisms grow | |
| 3. | A pyramid of numbers shows the | |
| A. | number of organisms at each stage in food chain | |
| B. | number of organisms in different food chains | |
| C. | number of food chains in a food web | |
| D. | total number of organisms in a food web | |
| 4. | Which of the following describes a community? | |
| A. | the total number of one species present | |
| B. | all the living organisms and the non-living parts | |
| C. | all the living organisms | |
| D. | all the plants | |
| 5. | Which of the following is a correct description of a decomposer? | |
| A. | A micro-organism which lives inside animals and causes disease | |
| B. | An organism which releases chemicals from organic waste | |
| C. | A fungus which grows on living tissue | |
| D. | A green plant which roots in rotting vegetation | |
| 6. | The biomass at each stage in a food chain decreases because | |
| A. | there are fewer organisms | |
| B. | the organisms are smaller | |
| C. | biomass is converted to waste | |
| D. | less energy is available for growth | |
| 7. | Why might a pyramid of biomass not have the same shape as a a pyramid of numbers for the same food chain? | |
| A. | the biomass is not always related to the number | |
| B. | the biomass depends on the number | |
| C. | the number depends on the energy available | |
| D. | the number is always greater than the biomasss | |
| 8. | Which food chain below would give a different pattern in a pyramid of biomass and a pyramid of numbers? | |
| A. | rose bush → greenfly → ladybird | |
| B. | algae → waterflea → fish | |
| C. | grass → rabbit → fox | |
| D. | seed → vole → kestrel | |
| 9. | The niche of an organism is | |
| A. | where it lives | |
| B. | its role in the habitat | |
| C. | the type of habitat where it is found | |
| D. | the number of organisms present | |
| 10. | Which of the following is not a description of a niche? | |
| A. | tiny decomposer in the soil | |
| B. | small bird of prey | |
| C. | microscopic floating producer | |
| D. | large black beetle | |
| 11. | An ecosystem is more stable when it has | |
| A. | only a few different members of each species | |
| B. | many different species | |
| C. | many members of each species | |
| D. | few different species | |
| 12. | Plants convert 1% of the light energy they receive into new plant material. In the food chain below, primroses receive 100 000 units of light energy. Primrose → vole → weasel → owl How much energy is available for the vole? | |
| A. | 10 000 units | |
| B. | 1000 units | |
| C. | 100 units | |
| D. | 10 units | |
| 13. | Animals that feed on both plants and animals are called … | |
| A. | carnivores | |
| B. | herbivores | |
| C. | detritivores | |
| D. | omnivores | |
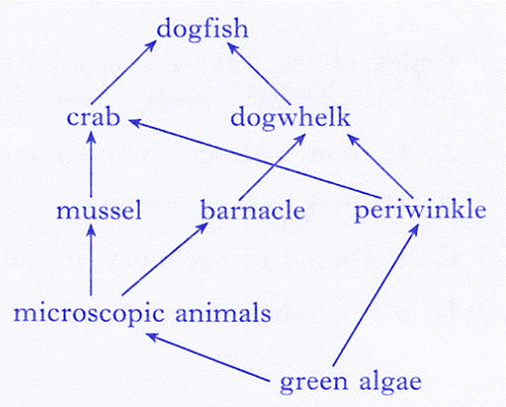
| 14. | The diagram below shows a food web from the seashore.
The mussel can be described as…… |
||||||
| A. | producer | B. | primary consumer | ||||
| C. | secondary consumer | D. | decomposer | ||||
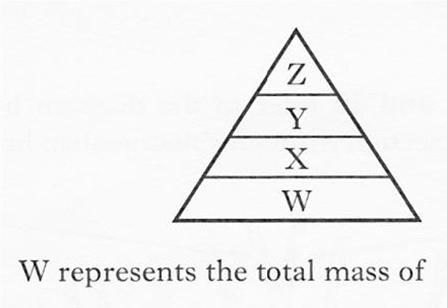
| 15. | The diagram below represents a pyramid of biomass.
|
||
| A. | producers | ||
| B. | prey | ||
| C. | predators | ||
| D. | herbivores | ||
| 16. | Which term describes all the organisms living in the same area? | |
| A. | food web | |
| B. | ecosystem | |
| C. | population | |
| D. | community | |
| 17. | Which term describes an animal that eats other animals in food web? | |
| A. | prey | |
| B. | predator | |
| C. | producer | |
| D. | primary consumer | |
| 18. | In a woodland ecosystem which of the following describes a population? | |
| A. | all the oak trees | |
| B. | all the plants | |
| C. | all the plants and animals | |
| D. | all the oak trees and blackbirds | |
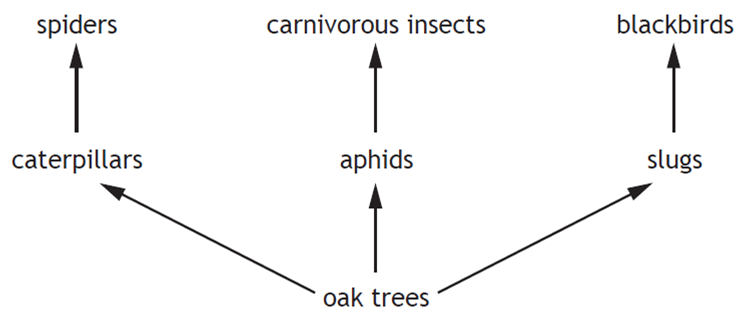
| 19. | The diagram below shows part of a food web in an oak woodland.
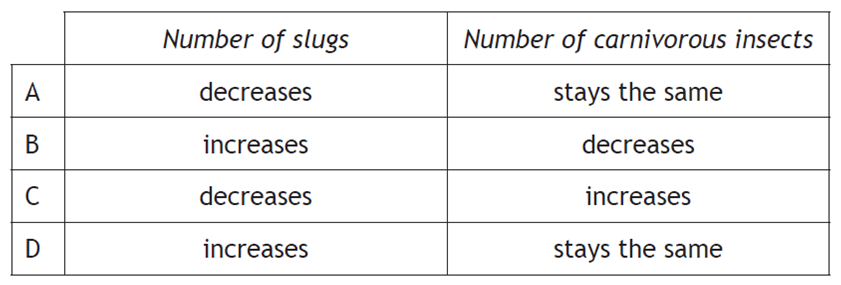
The use of insecticides in a nearby field resulted in the death of most aphids and caterpillars. Which line in the table identifies the effect on the numbers of slugs and carnivorous insects? |
||
| A. | A | ||
| B. | B | ||
| C. | C | ||
| D. | D | ||