| 1. | Which of the following stages in respiration would result in the production of 38 molecules of ATP? | |
| A. | Glucose to pyruvic acid | |
| B. | Pyruvic acid to lactic acid | |
| C. | Pyruvic acid to carbon dioxide and water | |
| D. | Glucose to carbon dioxide and water | |
| 2. | Which of the following stages in respiration would result in the production of 36 molecules of ATP? | |
| A. | Glucose to pyruvic acid | |
| B. | Pyruvic acid to lactic acid | |
| C. | Pyruvic acid to carbon dioxide and water | |
| D. | Glucose to carbon dioxide and water | |
| 3. | The type of energy in food is | |
| A. | heat | |
| B. | chemical | |
| C. | movement | |
| D. | kilojoules | |
| 4. | The type of energy released when food burns is mainly | |
| A. | heat | |
| B. | stored | |
| C. | chemical | |
| D. | movement | |
| 5. | Which unit is used to express the energy content? | |
| A. | cm | |
| B. | kJ | |
| C. | g | |
| D. | amps | |
| 6. | By which process is energy released from food in the cells of living organisms? | |
| A. | combustion | |
| B. | respiration | |
| C. | osmosis | |
| D. | photosynthesis | |
| 7. | Which food molecule is the main source of energy in cells? | |
| A. | glucose | |
| B. | protein | |
| C. | fat | |
| D. | starch | |
| 8. | Respiration is controlled by | |
| A. | glucose molecules | |
| B. | energy-releasing reactions | |
| C. | chemical energy | |
| D. | a series of enzymes | |
| 9. | During respiration, some of the energy in food molecules is transferred to the chemical energy of other molecules. The rest of the energy is released as | |
| A. | movement energy | |
| B. | sound energy | |
| C. | light energy | |
| D. | heat energy | |
| 10. | Which best represents ATP? | |
| A. | adenosine – P – P – P | |
| B. | adenosine – P – P | |
| C. | adenosine – P | |
| D. | adenosine – P – P – P – P | |
| 11. | Which change represents the way in which ATP is formed in cells? | |
| A. | ADP + energy → ATP + Pi | |
| B. | ADP + Pi + energy → ATP | |
| C. | ADP + Pi → ATP | |
| D. | ADP + Pi → ATP + energy | |
| 12. | Which change represents the way in which ATP is broken down in cells? | |
| A. | ATP → ADP + Pi + energy | |
| B. | ATP + energy → ADP + Pi | |
| C. | ATP + Pi → ADP + energy | |
| D. | ATP → ADP + Pi | |
| 13. | The energy for the formation of ATP in cells comes from | |
| A. | ADP | |
| B. | glucose | |
| C. | inroganic phosphate | |
| D. | enzymes | |
| 14. | The function of ATP in cells is to | |
| A. | make glucose | |
| B. | act as an enzyme | |
| C. | store food | |
| D. | act as an energy source | |
| 15. | A solution is added to muscle fibre. The fibre will contract if the solution is | |
| A. | glucose | |
| B. | ADP | |
| C. | ATP | |
| D. | phosphate | |
| 16. | A muscle fibre shrinks form 30mm down to 24mm. What is the percentage decrease in length? | |
| A. | 6% | |
| B. | 20% | |
| C. | 25% | |
| D. | 80% | |
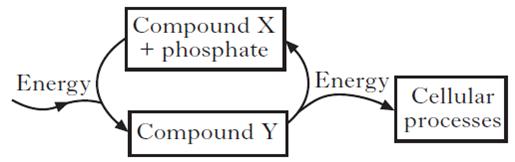
| 17. | The diagram below shows energy transfer within a cell. Compound X would be
|
||
| A. | ATP | ||
| B. | Glucose | ||
| C. | carbon dioxide | ||
| D. | ADP | ||
| 18. | The energy yield per glucose molecule during aerobic respiration is | |
| A. | 2 molecules of ATP | |
| B. | 18 molecules of ATP | |
| C. | 36 molecules of ATP | |
| D. | 38 molecules of ATP | |
| 19. | From what do animals obtain energy? | |
| A. | food | |
| B. | the sun | |
| C. | green plants | |
| D. | photosynthesis | |
| 20. | Which gas do animals need to carry out life processes? | |
| A. | Oxygen | |
| B. | Carbon monoxide | |
| C. | Helium | |
| D. | Carbon dioxide | |