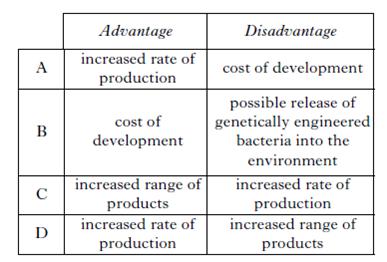
| 2. | Which line in the table below identifies correctly one advantage and one disadvantage of genetic engineering to make desired products?
|
||||||||||||
| A. | A | B. | B | C. | C | D. | D | ||||||
| 3. | Gentic engineering can be used to alter bacterial cells in order to produce human insulin.
|
||||||||||||
| A. | 1, 3, 4, 2 | B. | 1, 3, 2, 4 | C. | 3, 4, 2, 1 | D. | 3, 1, 2, 4 | ||||||
| 4. | Genetic engineering is the | |
| A. | swapping of genes between organisms | |
| B. | construction of new genetics of DNA | |
| C. | hybridising of different species | |
| D. | transfer of DNA from one organism to another | |
| 5. | The genes of an organism are made of | |
| A. | DNA | |
| B. | chromosomes | |
| C. | plasmids | |
| D. | cell nuclei | |
| 6. | The normal control of activity in a bacterium depends on | |
| A. | foreign genes | |
| B. | inserted plasmids | |
| C. | chromosomes | |
| D. | simple proteins | |
| 7. | Plasmids are used to | |
| A. | cut genes out of chromosomes | |
| B. | carry genes into bacterial cells | |
| C. | make protein in bacterial cells | |
| D. | join genes together | |
| 10. | Gene therapy is when | |
| A. | genes are given as medicines | |
| B. | proteins are used to make genes | |
| C. | new genes are made in the body | |
| D. | defective genes are replaced | |
| 11. | Gene therapy could cure cystic fibrosis because it is caused by | |
| A. | a missing chromosome | |
| B. | an extra chromosome | |
| C. | a defective gene | |
| D. | a harmful bacterium | |
| 12. | A genetically modified organism means an organism which has had genes | |
| A. | removed | |
| B. | added | |
| C. | replaced | |
| D. | divided | |
| 13. | GM crops offer many benefits. One of these is that | |
| A. | more fertilisers will be used | |
| B. | plants become more drought resistant | |
| C. | yields are reduced | |
| D. | weedkillers become less effective | |
| 17. | Which of the following is an example of a genetically engineered organism? | |
| A. | A plant that received external DNA to produce natural insecticides | |
| B. | A new plant variety created as a result of mutation | |
| C. | Seedless fruits resulting from sprayign the flowers with chemicals | |
| D. | A plant that naturally possesses medicinal properties | |
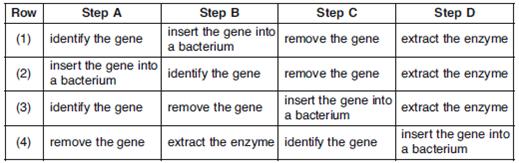
| 18. | In some people, the lack of a particular enzyme causes a disease. Scientists are attempting to use bacteria to produce this enzyme for the treatment of people with the disease. Which row in the chart below best describes the sequence of steps the scientists would most likely follow?
|
||||||||||||
| A. | 1 | B. | 2 | C. | 3 | D. | 4 | ||||||
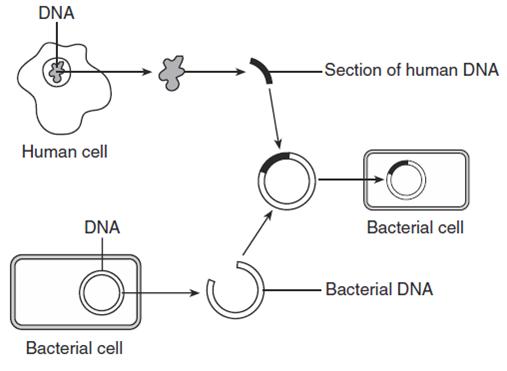
| 19. | The diagram below represents one technique used in biotechnology. The substance used to cut the bacterial DNA so that the human DNA could be inserted is a
|
||||||||||||
| A. | base | B. | enzyme | C. | phosphate group | D. | plasmid | ||||||
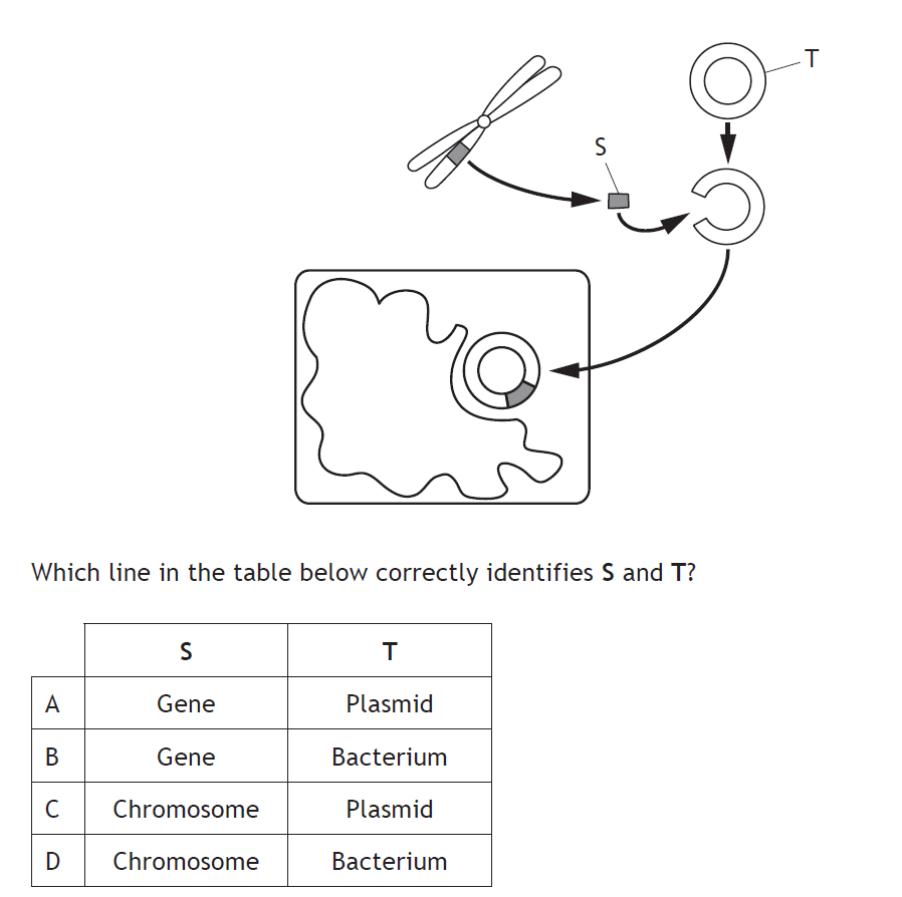
| 20. | The diagram below shows stages in the production of a substance, such as insulin, by genetic engineering.
|
||||||||||||
| A. | A | B. | B | C. | C | D. | D | ||||||