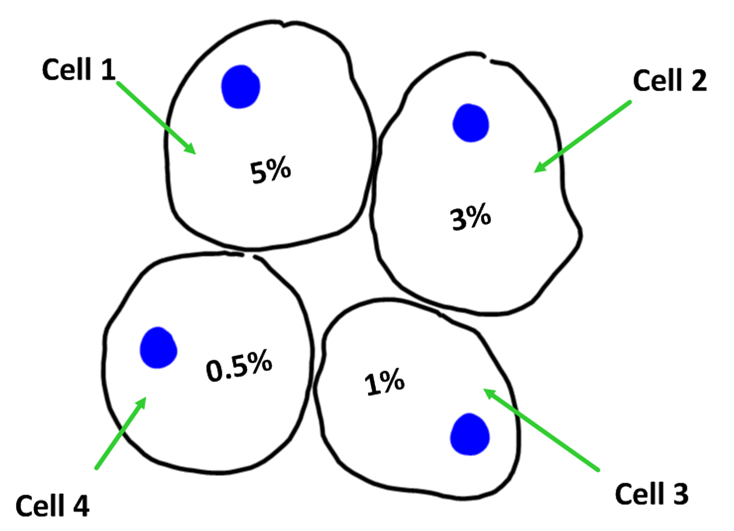
| 1. | In the diagram of 4 cells, the % solute concentration in each cell is given.
Water would move by osmosis from…. |
||||||||||||
| A. | cell 1 to cell 2 | B. | cell 2 to cell 3 | C. | cell 3 to cell 4 | D. | cell 4 to cell 1 | ||||||
| 2. | In which example in the table below will water move from X to Y by osmosis?
|
||
| Solute Concentration (%) | |||
| Solution X | Solution Y | ||
| A. | 3 | 8 | |
| B. | 8 | 3 | |
| C. | 3 | 1 | |
| D. | 3 | 3 |
| 4. | A plant cell, which was placed in a liquid, gained water by osmosis.When compared to the liquid, the cell contents are described as being | |
| A. | plasmolysed | |
| B. | hypertonic | |
| C. | hypotonic | |
| D. | flaccid | |
| 5. |
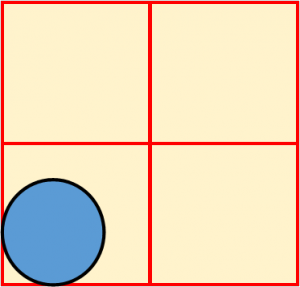
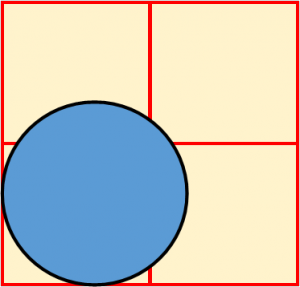
The diagram below shows the initial diameter of a potato disc. The potato disc was placed in a hypotonic solution for one hour.
Which of the diagrams below correctly shows the change in the diameter of the disc? |
||||||
| A. |
|
B. |
|
||||
| C. | 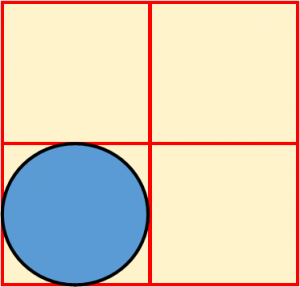 |
D. | 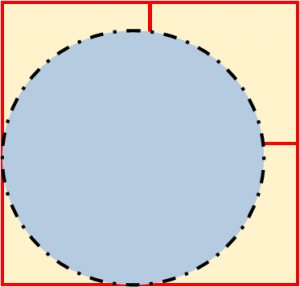 |
||||
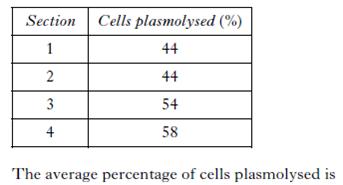
| 6. | Four thin sections of onion tissue were immersed in 5% sugar solution. The sections were left for 15 minutes then viewed under a microscope.The table below shows the percentage of cells plasmolysed in each section.
|
||||||||||||
| A. | 44 | B. | 50 | C. | 54 | D. | 200 | ||||||
| 7. | A piece of potato was cut from a potato tuber and weighed. It was placed in pure water for one hour and then removed, dried and weighed again. Finally, it was placed in a concentrated sugar solution for an hour, removed, blotted dry and weighed again.Which line in the table records the results which would most likely be obtained? |
||||
| First Weighing | Second Weighing | Third Weighing | ||
| A. | 5g | 6g | 4g | |
| B. | 5g | 4g | 6g | |
| C. | 6g | 5g | 4g | |
| D. | 5g | 4g | 3g |
| 8. | When animal cells are placed in a hypotonic solution they | |
| A. | remain unchanged | |
| B. | burst | |
| C. | become turgid | |
| D. | become plasmolysed | |
| 9. | Four thin sections of red cabbage tissue were immersed in a 5% sugar solution. The sections were left for 15 minutes then viewed under the microscope.The table shows the percentage of cells plasmolysed in each slide.
|
||||||||||||
| A. | 22 | B. | 25 | C. | 27 | D. | 100 | ||||||
| 10. | Which structural feature is common to both plant and animal cells? | |
| A. | Cell wall | |
| B. | Chloroplast | |
| C. | Nucleus | |
| D. | Large central vacuole | |
| 11. | What does a plant cell contain that an animal cell does not? | |
| A. | cytoplasm | |
| B. | nucelus | |
| C. | cell wall | |
| D. | cell membrane | |
| 12. | Both animal and plant cells usually have a | |
| A. | nucleus, cell membrane and cytoplasm | |
| B. | nucleus, cell wall and chloroplasts | |
| C. | nucleus, vacuole and cell wall | |
| D. | nucleus, cell wall and cytoplasm | |
| 13. | An important feature of the nucleus is that it | |
| A. | is full of water | |
| B. | has a round shape | |
| C. | contains information | |
| D. | makes a thin barrier | |
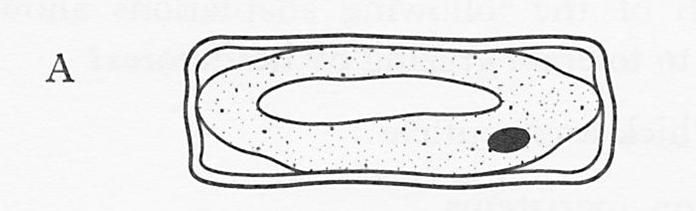
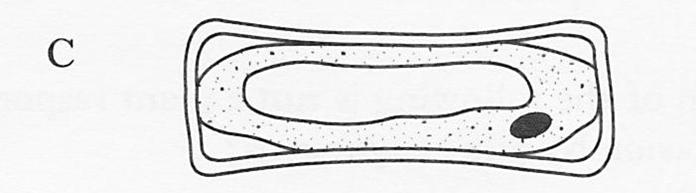
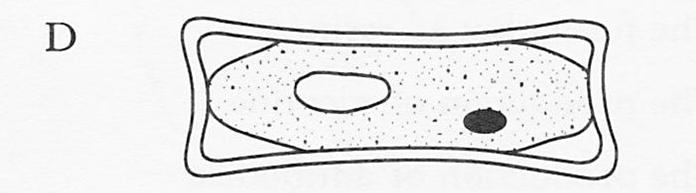
| 14. | The diagram below shows the appearance of a plant cell which had been placed in an isotonic solution.Which of the following diagrams best illustrates the cell after being immersed in a hypertonic solution?
|
||||||
| A. |
|
B. |
|
||||
| C. |
|
D. |
|
||||
| 15. | Visking tubing is selectively permeable. In the experiment shown below to demonstrate osmosis, the following results were obtained. Initial mass of visking tubing plus contents = 10.0g Mass of visking tubing plus contents after experiment = 8.2g. The results shown would be obtained when
|
||||||
| A. | R is 10% salt solution and S is water | B. | R is 5% salt solution and S is water | ||||
| C. | R is 10% salt solution and S is a 5% salt solution | D. | R is 5% salt solution and S is a 10% salt solution | ||||
| 16. | When a plant cell is immersed in a hypertonic solution it will | |
| A. | burst | |
| B. | become turgid | |
| C. | become flaccid | |
| D. | shrink | |
| 17. | When an animal cell is immersed in a hypertonic solution it will | |
| A. | become flaccid | |
| B. | burst | |
| C. | become turgid | |
| D. | shrink | |
| 18. | Red blood cells have a solute concentration of around 0.9%. What will happen to these cells when immersed in a 1% salt solution? | |
| A. | The cells will swell but not burst | |
| B. | The cells will shrink | |
| C. | The cells will remain unaffected | |
| D. | The cells will burst | |
| 19. | When an plant cell is immersed in a hypotonic solution it will | |
| A. | become flaccid | |
| B. | become turgid | |
| C. | shrink | |
| D. | burst | |
| 20. | Some peeled pieces of apple were placed in distilled water and some in very salty water.The cells in the apple pieces will — | |
| A. | lose water in both solutions | |
| B. | gain water in both solutions | |
| C. | lose water in the distilled water and gain water in the salty water | |
| D. | gain water in the distilled water and lose water in the salty water | |