Definitions
Space Travel
Newton’s 3rd Law
“Every action has an equal and opposite reaction”
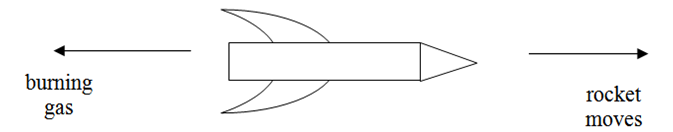
This law is used when dealing with the propulsion of rockets and spacecrafts:
The burning gas is forced backwards out of the rocket. At the same time the gas exerts a force on the rocket which is equal in size but opposite in direction. This force pushes the rocket forwards.
Newton’s 1st Law
“An object will remain stationary or will travel at a constant velocity, provided there are no unbalanced forces acting.”
A rocket in space will continue at a constant speed (even without boosters) since there is no air resistance or friction to slow it down.
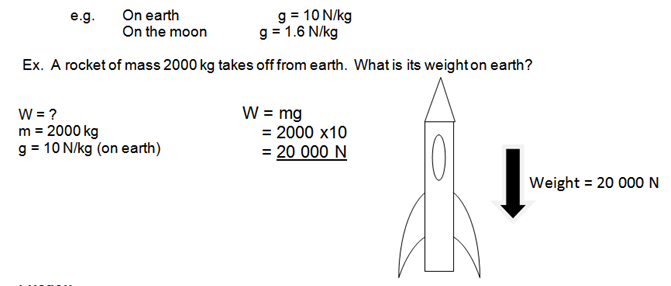
Mass and Weight
Mass is measured in kilograms (kg). It is a measure of the amount of matter making up an object. The mass of an object does not change.
Weight is measured in Newtons (N). It is the force on an object exerted by gravity. Weight will change depending on the gravitational field strength, g.
Friction
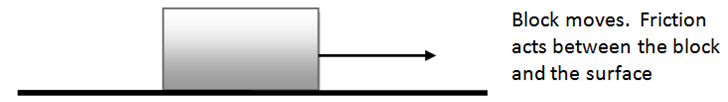
Friction is a force produced when two surfaces move over each other.
Friction is an opposing force. It acts against the motion of an object and will try to prevent an object moving.
Friction could be reduced here in a number of ways, e.g. using wheels or rollers.
In space travel, friction can be problematic during take-off. The rocket must be streamlined or aerodynamic to reduce friction due to air resistance.
On re-entry, friction between the rocket and the atmosphere causes the rocket to heat up. Heat shields are required to prevent the rocket from burning up.
On re-entry, friction is also helpful in slowing the rocket down.
Close to touch down, parachutes are used to increase air resistance (friction) and slow the rocket down further.
Life Elsewhere?
For life to exist on earth two things are required:
1. Liquid water
2. Oxygen rich atmosphere
Planets or moons that have liquid water may support life.
Planets outside our solar system are known as “exoplanets”. Many have now been discovered including some which may have liquid water.