1. C
2. D
3. C
4. B
5. A
6. A
7. C
8. D
9. D
10. C
| 11. |
|
|
Hydrogen bonding is present between ammonia molecules |
|
|
|
|
| 12. |
|
|
 |
|
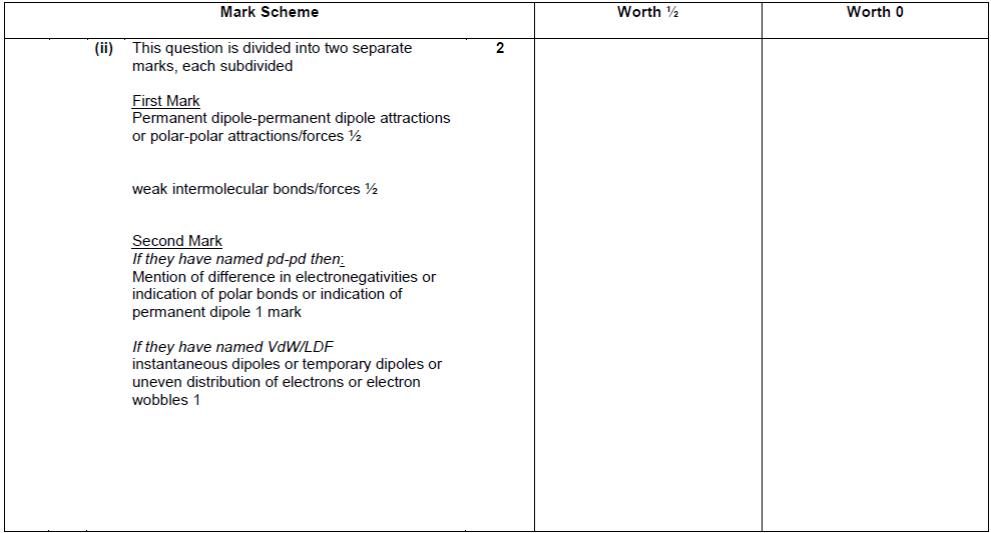 |
| 13. |
|
|
 |
|
|
| 14. |
|
|
Ethanol is an alcohol. The hydroxyl groups hydrogen bond with one another, giving ethanol higher melting and boiling points than propane.
Propane is an alkane. The forces holding these molecules together are weaker. The main force is van der Waals attraction, which, for these two compounds, is weaker than hydrogen bonding.
The London dispersion force is a temporary attractive force that results when the electrons in two adjacent atoms occupy positions that make the atoms form temporary dipoles. This force is sometimes called an induced dipole-induced dipole attraction.
Hydrogen bonds are permanent dipole-permanent dipole interactions.
Bonds consisting of a hydrogen atom bonded to an atom of a strongly electronegative element such as fluorine, oxygen or nitrogen are highly polar.
Hydrogen bonds are electrostatic forces of attraction between molecules which contain these highly polar bonds.
A hydrogen bond is stronger than other forms of permanent dipole-permanent dipole interactions but weaker than a covalent bond.
|
|
|
| 15. |
|
|
 |
|
|





